Unlocking the Secrets of Cannabinoids: Nature’s Hidden Compounds
In the intricate dance of nature’s chemistry, a group of compounds known as cannabinoids beckons with intriguing potential and promise. Unbeknownst to many, these molecular marvels play a pivotal role in the enigmatic relationship between plants and the human body. While often associated with the history of cannabis, cannabinoids extend their reach far beyond recreational use, intertwining with health, wellness, and the very fabric of our biological systems. As we embark on a journey to demystify these fascinating compounds, we’ll uncover their origins, functions, and the invaluable role they play in both therapeutic and everyday contexts. Join us as we explore what cannabinoids are, how they work, and why they continue to captivate scientists and wellness advocates alike.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Nature of Cannabinoids and Their Origins
- The Unique Interactions of Cannabinoids with the Human Endocannabinoid System
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in Modern Medicine
- Navigating the Legal Landscape and Responsible Use of Cannabinoids
- Q&A
- The Conclusion
Understanding the Nature of Cannabinoids and Their Origins
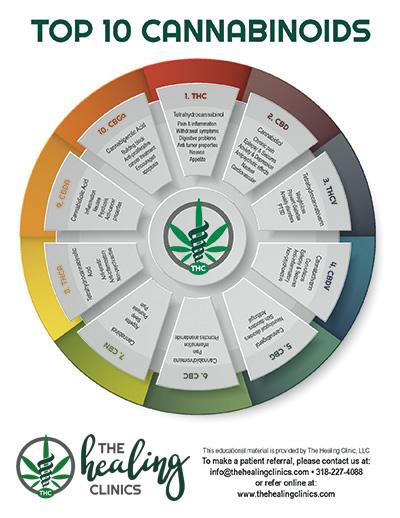
Cannabinoids are a diverse class of chemical compounds that play a pivotal role in the functioning of the endocannabinoid system, which is responsible for maintaining homeostasis within the body. These compounds can be naturally occurring or synthetic, and they interact with receptors throughout the body to produce a variety of physiological effects. The two most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), each with distinct properties and uses. While THC is primarily recognized for its psychoactive effects, CBD has gained popularity for its potential therapeutic benefits without producing a ‘high.’
Cannabinoids can be categorized into three main groups based on their origins:
- Phytocannabinoids: Found in the cannabis plant; these are the most well-studied and include both THC and CBD.
- Endocannabinoids: Naturally produced by the human body; these molecules help regulate various physiological processes.
- Synthetic cannabinoids: Man-made compounds designed to mimic natural cannabinoids, often used in research and in certain medical applications.
The understanding of cannabinoids has expanded dramatically in recent years, shedding light on their complex interactions and the myriad benefits they may offer. Here’s a snapshot of some key cannabinoids:
| Cannabinoid | Source | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|
| THC | Phytocannabinoid | Psychoactive, pain relief, appetite stimulation |
| CBD | Phytocannabinoid | Anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, neuroprotective |
| Anandamide | Endocannabinoid | Mood regulation, pain relief, memory |
| JWH-018 | Synthetic | Psychoactive effects, often linked to legal highs |
The Unique Interactions of Cannabinoids with the Human Endocannabinoid System
Cannabinoids are fascinating compounds that interact intricately with the human endocannabinoid system (ECS), a fundamental component that regulates a myriad of physiological processes. The ECS comprises endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes that work in tandem to maintain homeostasis. Notably, the two primary receptors, CB1 and CB2, play distinct roles: CB1 is predominantly found in the brain and central nervous system, influencing mood and cognition, while CB2 resides mainly in the immune system, modulating inflammation and pain response. This unique mapping of receptors allows cannabinoids to exert targeted effects, tailoring their influence based on where in the body they are active.
Moreover, cannabinoids are not created equal; each type communicates with the ECS in varied ways. Some cannabinoids, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), mimic natural endocannabinoids and can activate receptors to produce psychoactive effects. In contrast, CBD (cannabidiol) does not directly bind to these receptors but instead influences the ECS by enhancing the body’s own endocannabinoids. This distinctive mechanism helps to explain why different cannabinoids can offer diverse therapeutic benefits, making the study of their interactions with the ECS an exciting frontier in cannabis research. Understanding these subtleties is key to unlocking their full potential for health and wellness.
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in Modern Medicine
Cannabinoids are a fascinating class of compounds derived from the cannabis plant, known for their ability to interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system. This intricate system plays a critical role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, memory, appetite, and pain sensation. As researchers delve deeper into the pharmacological properties of cannabinoids, they have uncovered a wide range of potential therapeutic applications, including:
- Chronic Pain Management: Cannabinoids may help alleviate pain by modifying pain signaling pathways.
- Neurological Disorders: Research suggests potential benefits for conditions like epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
- Anxiety and Depression: Certain cannabinoids exhibit anxiolytic properties, offering hope for mental health treatments.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Cannabinoids have been shown to reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for various disorders.
What makes cannabinoids particularly appealing in modern medicine is their diverse chemical profile. The two most studied cannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), exhibit different effects on the body, allowing for tailored therapeutic approaches. The growing acceptance of cannabinoid-based treatments has prompted a surge in clinical studies exploring their efficacy and safety. Below is a simplified comparison of these two primary cannabinoids:
| Cannabinoid | Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| THC | Psychotropic, pain relief | Appetite stimulation, nausea relief |
| CBD | Non-psychotropic, anti-inflammatory | Seizure disorders, anxiety reduction |
Navigating the Legal Landscape and Responsible Use of Cannabinoids
As the landscape of cannabinoid usage evolves, understanding the myriad of legal frameworks becomes crucial for consumers and businesses alike. The legality of cannabinoids varies significantly depending on geographical location and various regulatory factors, including federal, state, and local laws. It is essential for individuals to stay informed about the specific regulations that apply to their region, considering aspects such as licensing, distribution, possession limits, and medical versus recreational use. These legal parameters can influence everything from the cultivation of hemp to the sale of cannabinoid-infused products, creating a dynamic environment that requires constant vigilance.
Being a responsible participant in the cannabinoid market also encompasses ethical considerations, including informed consumption and respect for the community. Adopting best practices can mitigate potential risks associated with improper use or distribution of these substances. Consumers should prioritize purchasing products from reputable sources that provide clear information on potency, ingredient transparency, and lab testing results. Community education and advocacy also play critical roles in shaping a positive perception of cannabinoids; fostering a well-informed public supports safe practices and a sustainable market. Below is a concise overview of key legal considerations:
| Aspect | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Ownership | Understand personal limits on possession |
| Distribution | Know the regulations for selling cannabinoids |
| Use | Differentiate between medical and recreational use |
| Product Safety | Seek lab-tested and reliable products |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Cannabinoids
Q: What exactly are cannabinoids?
A: Cannabinoids are a diverse group of compounds that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network responsible for regulating various physiological processes. Found primarily in the cannabis plant, cannabinoids can also be synthesized in the lab.
Q: How many types of cannabinoids are there?
A: There are over 100 known cannabinoids. The most well-studied and recognized types include THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC is known for its psychoactive properties, while CBD is praised for its potential therapeutic benefits without the high.
Q: What is the endocannabinoid system and why is it important?
A: The endocannabinoid system is an essential biological system that helps maintain homeostasis within the body. It consists of receptors, endocannabinoids (the body’s own cannabinoids), and enzymes that break down these compounds. This system plays a critical role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, pain sensation, and more.
Q: How do cannabinoids work in the body?
A: Cannabinoids work by binding to specific receptors in the endocannabinoid system, primarily CB1 and CB2 receptors. This interaction can influence various physiological processes, resulting in a range of effects from pain relief to mood enhancement.
Q: Are cannabinoids only found in cannabis?
A: While the cannabis plant is the most well-known source of cannabinoids, other plants and even synthetic processes can produce similar compounds. For example, some researchers are exploring cannabinoids in hemp and other botanicals, along with lab-created cannabinoids that mimic natural ones.
Q: What are the potential benefits of cannabinoids?
A: Cannabinoids have been studied for a variety of potential benefits, including pain management, reducing inflammation, alleviating anxiety and depression, and helping with sleep disorders. However, research is ongoing, and results can vary significantly from person to person.
Q: Are there any risks associated with cannabinoid use?
A: Yes, while cannabinoids can offer various benefits, there are potential risks. THC, for example, can induce psychoactive effects that may lead to anxiety, paranoia, or impaired motor function. Long-term or excessive use of cannabinoids may also lead to dependency or other adverse effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable before using cannabinoid products, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or those on medication.
Q: How is the legal status of cannabinoids evolving?
A: The legal status of cannabinoids is rapidly changing around the world. While CBD derived from hemp is legal in many places, THC remains subject to strict regulations. The increasing recognition of their medicinal properties has led to a push for greater access and research, but laws vary widely, making it important for users to stay informed based on their region.
Q: What’s the future of cannabinoid research?
A: The future of cannabinoid research looks promising, with increasing interest from both the scientific community and consumers. Researchers are exploring the potential of cannabinoids in treating a variety of ailments, understanding their long-term effects, and developing new cannabinoid-based therapies. As attitudes shift and more studies are conducted, we may uncover even more about these fascinating compounds.
The Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of cannabinoids, it’s clear that these fascinating compounds represent much more than mere components of the cannabis plant. From their intricate interaction with our endocannabinoid system to their potential therapeutic benefits, cannabinoids invite us to reconsider our understanding of wellness and healing. As research continues to unfold, the dialogue surrounding cannabinoids will likely evolve, opening doors to new possibilities and transforming perceptions about their role in healthcare. Whether one is a seasoned advocate or a curious newcomer, the journey into the world of cannabinoids encourages a deeper understanding of their complexities and the promises they hold. In a landscape that is continuously changing, one thing remains certain: cannabinoids are here to stay, paving the way for an enlightening future in both science and medicine.