Unraveling THC: A Journey Through Cannabis Chemistry
In a world where cannabis is increasingly celebrated for its multifaceted benefits, the spotlight often falls on one of its most intriguing components: tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC. This potent compound, renowned for its psychoactive properties, has been the subject of curiosity and research, sparking debates and discussions across cultural, medical, and legal landscapes. But what exactly is THC, and how does it interact with our bodies? In this article, we will delve into the science behind THC, exploring its origins, effects, and the ongoing exploration of its potential benefits and risks. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the complexities of THC, shedding light on its role in the ever-evolving narrative of cannabis.
Table of Contents
- Understanding THC and Its Origins in Cannabis
- Exploring the Effects of THC on Body and Mind
- Legal Considerations and Responsible Use of THC
- Navigating Dosing and Consumption Methods for Optimal Experience
- Q&A
- To Wrap It Up
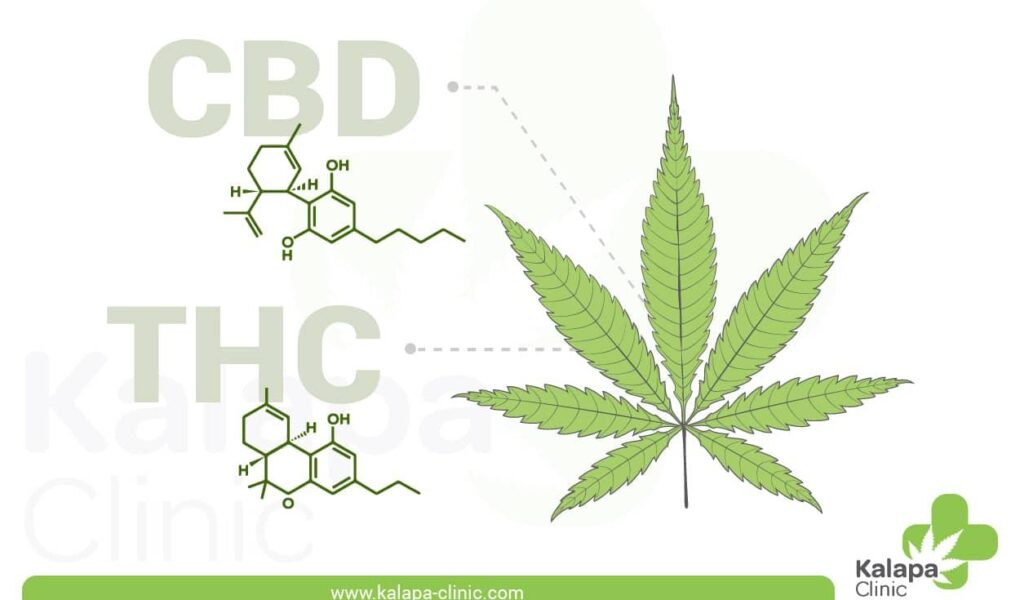
Understanding THC and Its Origins in Cannabis
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis, famous for its psychoactive effects. This compound interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the human body, specifically binding to CB1 receptors primarily located in the brain. The psychoactive nature of THC is responsible for the “high” experience associated with cannabis consumption. Beyond its recreational appeal, THC also possesses potential therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction, which have begun to attract scientific interest and medical exploration.
THC’s origins can be traced back thousands of years, with historical evidence suggesting that ancient cultures utilized cannabis for various purposes, including medicinal and spiritual practices. In modern times, the cultivation of cannabis has led to the emergence of various strains, each with unique profiles of cannabinoids and terpenes. Factors influencing the concentration of THC in cannabis plants include genetics, environmental conditions, and cultivation techniques. As research continues to unfold, our understanding of THC’s properties and its interaction with other cannabinoids may pave the way for enhanced therapeutic applications and refined cultivation methods.
Exploring the Effects of THC on Body and Mind
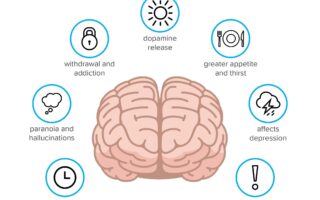
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, known for eliciting a range of effects on both the body and the mind. Users often report sensations of euphoria and relaxation, stemming from THC’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system, which plays a critical role in regulating mood, perception, and appetite. The effects can vary significantly between individuals, influenced by factors such as dosage, strain, and individual biology. Some common effects include:
- Increased Sensory Perception: Many users experience heightened awareness of sounds, colors, and tastes.
- Altered Time Perception: THC can make time seem to slow down, impacting decision-making.
- Relaxation and Euphoria: A sense of well-being is prevalent, often reducing anxiety for many users.
- Increased Appetite: Commonly referred to as “the munchies,” many find themselves craving food.
The physical effects of THC can range from mild to intense, depending on the individual’s tolerance and the consumption method. Physiologically, THC binding to cannabinoid receptors can result in various outcomes, with some users enjoying the calming effects, while others may experience discomfort such as heightened heart rate or dry mouth. Here’s a brief overview of key physical effects:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Heart Rate | Temporary elevation, often noticeable shortly after consumption. |
| Bloodshot Eyes | A common side effect due to vasodilation. |
| Dizziness | Can occur in new users or with higher doses. |
| Relaxed Muscles | May aid in relieving tension and discomfort. |
Legal Considerations and Responsible Use of THC
When considering the incorporation of THC into one’s lifestyle, it is essential to navigate the complex landscape of legal regulations. The legal status of THC varies dramatically across different states and countries, requiring individuals to remain vigilant and informed. Compliance with local laws is crucial not only to avoid potential legal repercussions but also to foster a culture of responsible usage. Here are key factors to keep in mind:
- Legal Status: Check if THC is legal in your area for medicinal or recreational use.
- Age Restrictions: Ensure you meet the legal age requirement to possess or consume THC products.
- Licensing: Purchase products from licensed dispensaries to guarantee quality and legality.
- Possession Limits: Be aware of the legal limits for possession to avoid fines and penalties.
In addition to legal aspects, responsible use of THC also encompasses understanding its effects and potential risks. THC can impair cognitive and motor functions, making it essential to consider your surroundings and activities when using. Take note of the following responsible use recommendations:
| Guidelines | Description |
|---|---|
| Start Low, Go Slow | Begin with a smaller dose to evaluate your tolerance. |
| Avoid Driving | Do not operate vehicles or heavy machinery after consumption. |
| Stay Hydrated | Drink water to mitigate dry mouth and enhance your experience. |
Navigating Dosing and Consumption Methods for Optimal Experience
Understanding the importance of dosing and consumption methods is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their experience with THC. Each individual’s response to cannabis can vary significantly based on several factors, including body chemistry, tolerance, and the method of consumption. Below are some common methods of THC consumption along with their typical effects:
- Smoking: Fast-acting, effects felt within minutes but can be short-lived.
- Vaping: Also quick to take effect and offers potentially fewer harmful byproducts than smoking.
- Edibles: Delayed onset (usually 30 minutes to 2 hours), but longer-lasting effects.
- Tinctures: Sublingual absorption provides relatively quick effects, customized dosing via dropper.
- Topicals: Non-intoxicating, ideal for localized effects without entering the bloodstream.
When it comes to dosing, it’s essential to start low and go slow. New users may consider beginning with minimal amounts, especially with edibles, to avoid overwhelming effects. The following table summarizes recommended starting doses based on different consumption methods:
| Consumption Method | Starting Dose |
|---|---|
| Smoking/Vaping | 1-2 puffs |
| Edibles | 2.5-5 mg THC |
| Tinctures | 1-2 drops |
| Topicals | Apply as needed |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding THC – The Basics
Q1: What is THC?
A1: THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive component found in the cannabis plant. It interacts with the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain, producing effects commonly associated with a “high,” such as euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception.
Q2: How does THC interact with the body?
A2: THC binds to cannabinoid receptors, mainly CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2 receptors found in the immune system. This interaction leads to various physiological and psychological effects, influencing mood, appetite, memory, and pain perception.
Q3: Can THC be used for medicinal purposes?
A3: Yes, THC has several therapeutic applications. It is often used in medical cannabis to alleviate chronic pain, reduce nausea in chemotherapy patients, stimulate appetite in those with wasting syndromes, and manage muscle spasticity in conditions like multiple sclerosis.
Q4: Is THC legal everywhere?
A4: No, the legal status of THC varies significantly across different regions. While some countries and states have legalized THC for recreational or medicinal use, others still classify it as a controlled substance. Always check local laws to ensure compliance before using THC products.
Q5: What are the side effects of THC?
A5: While many users enjoy the effects of THC, it can also produce side effects, including dry mouth, red eyes, increased heart rate, and anxiety in some individuals. Overconsumption may lead to temporary disorientation or paranoia, particularly in inexperienced users.
Q6: How is THC consumed?
A6: THC can be consumed in various forms, including smoking cannabis flowers, vaping, ingesting edibles, and using tinctures or oils. Each method of consumption has different onset times and effects, allowing users to select their preferred method based on their needs.
Q7: What is the difference between THC and CBD?
A7: THC and CBD (cannabidiol) are both cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, but they have distinct effects. THC is psychoactive, producing a “high,” while CBD is non-psychoactive and is often sought for its potential therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects associated with THC.
Q8: Can you develop a tolerance to THC?
A8: Yes, regular users of THC may develop a tolerance over time, meaning they might need to consume larger amounts to achieve the same effects. Tolerance can vary between individuals, and some may choose to take breaks to reset their sensitivity to THC.
Q9: Is there a difference between marijuana and hemp regarding THC?
A9: Absolutely! Marijuana is typically cultivated to contain high levels of THC (above 0.3%), making it suitable for recreational and medical use. Conversely, hemp is defined as cannabis that contains 0.3% THC or less, making it non-psychoactive and legal in many jurisdictions for industrial purposes, such as fiber, oil, and CBD extraction.
Q10: What should beginners know before trying THC?
A10: Beginners should approach THC with caution. It’s advisable to start with a low dose, particularly with edibles, as their effects take longer to kick in. It’s also essential to consider your setting and mental state, as a comfortable environment can significantly enhance the experience. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns or pre-existing conditions.
To Wrap It Up
understanding THC is more than just grasping a chemical formula; it’s about exploring the intricate tapestry of nature’s design and human experience. As we’ve delved into its effects on the body and mind, the myriad of uses, and the ongoing research shedding light on its potential, it’s clear that THC holds a prominent place in both therapeutic applications and cultural conversations. Whether you’re a seasoned enthusiast or just beginning to uncover the layers of cannabis, recognizing the role THC plays in this evolving narrative can empower you to make informed decisions. As science continues to advance, and societal perspectives shift, the journey into the world of THC is just beginning. Let this knowledge guide you towards a deeper appreciation of the complexities that lie within this remarkable compound.