In the sprawling tapestry of nature, few plants have sparked as much curiosity and conversation as the marijuana plant. With its intricate leaves, distinct aroma, and versatile applications, Cannabis sativa stands not only as a botanical wonder but also as a cultural phenomenon. From medicinal uses that trace back thousands of years to its contemporary status as a symbol of both healing and recreation, understanding the marijuana plant involves delving into a fascinating interplay of biology, history, and societal evolution. In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore the various attributes of the marijuana plant, examining its physical characteristics, growth patterns, and the unique environments in which it thrives. Whether one is seeking knowledge for cultivation or simply to satisfy a curiosity, this comprehensive description aims to illuminate the essence of a plant that continues to shape our world in myriad ways.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Anatomy of the Marijuana Plant
- Identifying Varieties: The Spectrum of Cannabis Strains
- Cultivation Tips for Thriving Marijuana Plants
- Harvesting and Post-Harvest Care for Optimal Quality
- Q&A
- Insights and Conclusions
Understanding the Anatomy of the Marijuana Plant
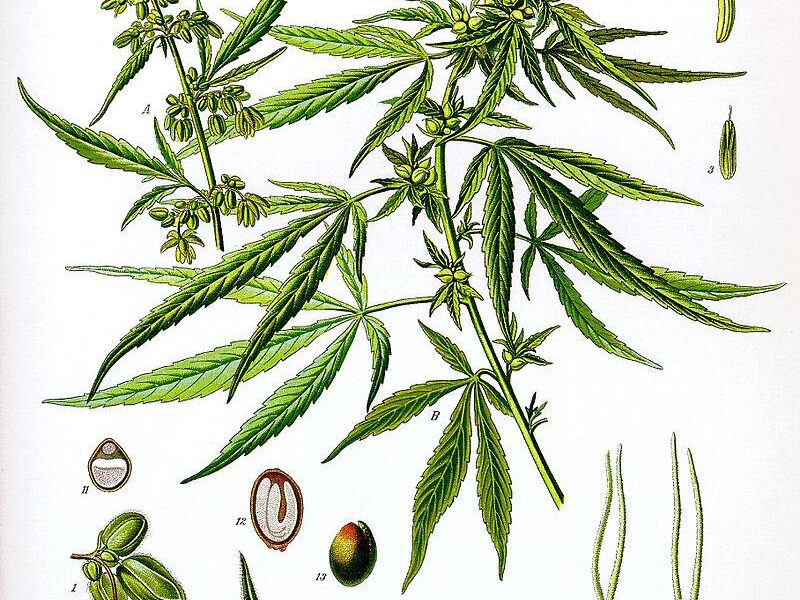
The marijuana plant is a fascinating organism, rich in biology and diversity. Comprised of several key parts, each plays a distinct role in its overall function and impact. The roots anchor the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, while the stem serves as a central support structure, facilitating nutrient transportation. Above ground, the plant showcases its most recognizable feature, the leaves, which are serrated and palm-like, optimizing sunlight capture for energy through photosynthesis. Additionally, the flowers, or buds, are where the magic happens – housing cannabinoids and terpenes that contribute to the plant’s psychoactive properties and distinctive aroma.
Understanding the anatomy extends into the reproductive structures, where you’ll find the male and female flowers. Female plants are sought after for their resinous buds, often brimming with rich trichomes. The process of pollination is crucial, as it determines whether the plant will bear seeds or produce sinsemilla, seedless cannabis, which is usually higher in potency. The following table summarizes the key components of the marijuana plant along with their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Roots | Absorb water and nutrients |
| Stem | Support and transport nutrients |
| Leaves | Photosynthesis for energy |
| Flowers (Buds) | Production of cannabinoids and terpenes |
| Male/Female Flowers | Pollination and reproduction |
Identifying Varieties: The Spectrum of Cannabis Strains
The world of cannabis is as diverse as it is fascinating, with each strain boasting unique characteristics that cater to various preferences and medicinal needs. Cannabis can be broadly categorized into three primary types: Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid. Indica strains are typically associated with relaxation and sedative effects, often preferred for nighttime use to help with sleep and anxiety. On the other hand, Sativa strains tend to energize and uplift the user, making them ideal for daytime use and creativity. Hybrids, which are a blend of both Indica and Sativa, offer a tailored experience—providing the best of both worlds, depending on the specific traits of the parent strains.
Understanding the differences among these categories can assist consumers in making informed choices. Beyond Indica and Sativa, the nuances within individual strains are essential. Strains are distinguished by their aroma, flavor, and effects, influenced by their terpene and cannabinoid profiles. For example, a Lemon Haze strain is often celebrated for its citrusy scent and uplifting properties, while a Granddaddy Purple is renowned for its deep grape-like flavor and relaxing qualities. The table below summarizes some popular strains and their primary effects:
| Strain Name | Type | Primary Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Dream | Hybrid | Balanced relaxation and euphoria |
| Girl Scout Cookies | Hybrid | Creative and happy sensation |
| OG Kush | Indica | Stress relief and sleepy vibes |
| Sour Diesel | Sativa | Energizing and cerebral high |
Cultivation Tips for Thriving Marijuana Plants
To cultivate vibrant marijuana plants, the right environment and care practices are essential. Start with selecting a well-draining soil enriched with organic matter. Use pots with adequate drainage holes to prevent root rot. Regular watering is crucial, aiming for even moisture but avoiding waterlogging. Remember, marijuana thrives in sunny locations; therefore, ensure your plants receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Consider utilizing grow lights if you’re growing indoors. Additionally, keep an eye on the temperature, ideally between 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C) during the day, and slightly cooler at night.
Feeding your plants with the right nutrients is vital for their growth and robustness. Begin with a balanced nutrient solution during the vegetative stage, leaning toward higher nitrogen levels. Transition to a bloom formula as your plants start flowering, focusing on phosphorus and potassium for enhancing bud development. Implementing a proper pruning technique encourages bushier growth and improves airflow around the plants. Lastly, always monitor for pests and diseases, implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to maintain a healthy growing environment.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Care for Optimal Quality
Successfully harvesting marijuana requires a careful approach to ensure that the quality of the buds is maximized. Timing is crucial; the optimal moment to harvest is when the trichomes shift from clear to a milky white color, indicating peak potency. During the cutting process, it’s essential to use sharp, sterile tools to avoid damaging the plant and to reduce the risk of disease. Additionally, they should be cut in a way that prevents unnecessary stress on the remaining plant material. Once harvested, the marijuana should be transferred to a clean, dry area where airflow is abundant to prevent mold formation.
Post-harvest care extends to the drying and curing stages, pivotal for enhancing flavor and potency. It is advisable to hang the branches upside down in a dark, well-ventilated space with a humidity level of around 50-60%. After approximately 7-14 days of drying, the buds should feel dry on the outside but slightly moist on the inside. At this stage, it’s time to cure the cannabis by placing it in airtight containers. This process should be undertaken over several weeks, where the buds are opened daily to allow fresh air exchange, further improving their characteristics. A few tips for priority include:
- Control Temperature: Keep the drying area between 60-70°F to further reduce the chance of mold.
- Monitor Humidity: Use hygrometers in curing jars to maintain levels at about 62%.
- Patience is Key: Curing for at least 4-8 weeks can lead to significantly better flavor profiles.
Q&A
Q: What does a cannabis plant look like?
A: A cannabis plant boasts a distinctive appearance, characterized by its tall, slender stature that can reach heights of up to 12 feet or more, depending on the strain and growing conditions. Its lush green leaves are typically hand-shaped, featuring serrated edges that create an iconic silhouette. The most recognizable varieties of leaves generally have seven to nine leaflets radiating from a central stem, each a vibrant green, sometimes even appearing purple or yellow under certain environmental influences.
Q: How can I distinguish between male and female cannabis plants?
A: During the pre-flowering stage, male and female cannabis plants can be quite similar in their foliage, but subtle differences emerge as they mature. Male plants typically develop small, round pollen sacs that resemble tiny balls, while female plants start to exhibit white pistils—hair-like structures that emerge from the calyx of the bud. As the flowering phase progresses, the female plants become fuller and denser, forming large, resinous buds that are prized for their potency.
Q: What role does the environment play in the development of a cannabis plant?
A: The environment exerts a profound influence on the growth and characteristics of a cannabis plant. Factors such as light, temperature, humidity, and soil quality can determine not just the size and symmetry of the plant, but also the cannabinoid and terpene profiles. For instance, a plant grown in optimum conditions may exhibit vibrant colors and robust growth, while subpar conditions can deter photosynthesis and limit development.
Q: Do different strains of cannabis have different appearances?
A: Absolutely! The cannabis family is diverse, with different strains showcasing a range of colors, leaf shapes, and bud structures. Indica strains might appear shorter and bushier, while sativa strains often stretch tall and slender. Some strains carry hues of deep purple or bright orange, derived from variations in their chlorophyll and anthocyanin content. Each strain carries its own unique fingerprint, reflecting the genetics and cultivation techniques employed.
Q: What are trichomes, and what purpose do they serve?
A: Trichomes are tiny, hair-like structures that cover the surface of cannabis buds and leaves. They appear as shiny, crystal-like formations and come in three types: bulbous, capitate-sessile, and capitate-stalked. Trichomes serve a critical purpose for the plant, as they produce the essential oils, cannabinoids, and terpenes that contribute to the plant’s aroma, flavor, and psychoactive properties. They also act as a protective layer, deterring pests and environmental stressors.
Q: Can the color of a cannabis plant indicate anything about its quality?
A: While color can be a visual cue in assessing the health of a cannabis plant, it isn’t a definitive measure of quality. Healthy cannabis tends to be a rich, vibrant green. However, discoloration can result from nutrient deficiencies, overexposure to light, or environmental stressors, leading to yellowing or browning leaves. While striking colors can enhance visual appeal—think of vivid purples or fiery reds—they should be assessed alongside other factors like aroma, texture, and trichome development to gauge overall quality.
Q: How should I care for my cannabis plants for optimal growth?
A: Caring for cannabis plants effectively hinges on a combination of proper light exposure, adequate watering, and nutrient management. Regular monitoring of soil moisture and nutrient levels is essential, as both over or under-saturation can impede growth. Additionally, pruning techniques and supporting structures can help shape the plant for maximum light exposure, promoting healthier yields. Each stage of growth—seedling, vegetative, and flowering—comes with specific care requirements, all of which contribute to the overall vitality of the plant.
Insights and Conclusions
the marijuana plant is a remarkable botanical specimen with a rich history and a diverse array of characteristics. From its intricate leaf structures to its varied cannabinoid profiles, each aspect of this multifaceted plant tells a story of adaptation and utility. Whether you view it through the lens of pharmacology, horticulture, or cultural significance, understanding the marijuana plant opens the door to a deeper appreciation of its role in our world. As more research unfolds and society continues to evolve in its relationship with cannabis, the importance of accurately describing and understanding this plant becomes ever more crucial. So, as you embark on your journey of exploration, remember that every leaf and blossom holds a wealth of knowledge waiting to be discovered.