As the boundaries of science and culture increasingly collide in the realm of cannabis, one question continues to pique the curiosity of both enthusiasts and newcomers alike: Is THC a chemical? Tetrahydrocannabinol, better known as THC, is frequently referenced in conversations about marijuana and its effects, yet its classification often sparks confusion. In this exploration, we will dissect the very essence of THC, delving into its chemical structure, its role within the cannabis plant, and its effects on human physiology. Join us on this enlightening journey as we uncover the intricate world of cannabinoids, unravel the scientific lingo, and clarify the standing of THC within the broader context of chemical compounds.
Table of Contents
- Understanding THC: A Deep Dive into Its Chemical Structure
- The Role of THC in the Cannabis Plant and Its Effects on the Body
- Potential Benefits and Risks of THC Consumption
- Guidelines for Responsible Use and Further Research Recommendations
- Q&A
- The Conclusion
Understanding THC: A Deep Dive into Its Chemical Structure
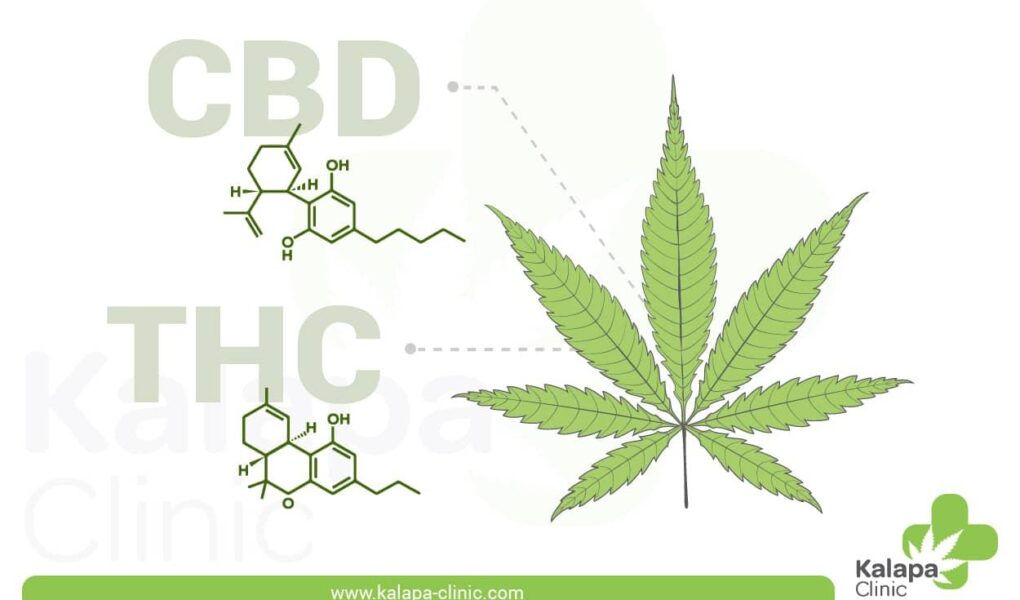
Understanding the Chemical Backbone of THC begins with its molecular formula, C21H30O2. This potent compound consists of twenty-one carbon atoms, thirty hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. The unique arrangement of these atoms creates a specific three-dimensional shape that is crucial for its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system. In simpler terms, it is how the atoms are connected and arranged that ultimately dictates THC’s effects on the mind and body. The chemical structure features a phenolic ring, a cyclohexene ring, and a long aliphatic side chain, which are essential for its classification as a psychoactive substance.
Deciphering THC’s Role in the Body reveals the importance of its chemical structure in mediating various physiological responses. THC predominantly interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain, which are part of the endocannabinoid system that regulates many bodily functions. The design of THC allows it to mimic natural neurotransmitters like anandamide, leading to various effects, from euphoria to altered sensory perception. Understanding its chemical structure not only illuminates why THC generates these psychoactive effects but also opens the door to potential medical applications, ranging from pain management to appetite stimulation. The ever-evolving research into THC’s properties underscores the importance of its chemical composition in both recreational and therapeutic settings.
The Role of THC in the Cannabis Plant and Its Effects on the Body
Thc, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is one of over 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, playing a pivotal role in the distinctive effects associated with its consumption. This naturally occurring compound interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which regulates various physiological processes. Some of the most notable effects of THC include:
- Psychoactive Effects: THC is primarily known for producing the “high” that comes from smoking or consuming cannabis.
- Appetite Stimulation: Often referred to as the “munchies,” THC can significantly increase hunger levels.
- Pain Relief: Many users report that THC helps manage chronic pain conditions.
- Anxiety and Mood Regulation: Depending on the quantity consumed, THC may alleviate anxiety in some individuals, while it can trigger it in others.
The *medical utilization* of THC has been a focal point of research, with studies suggesting that it may provide therapeutic benefits for a range of conditions, including but not limited to:
| Condition | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chronic Pain | Pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects |
| Insomnia | Improved sleep quality |
| Anxiety Disorders | Potential reduction in anxiety levels |
| Nausea | Reduction of chemotherapy-related nausea |
The dual nature of THC’s effects amplifies the importance of mindful consumption, especially considering its interaction with individual body chemistry and existing medical conditions. Understanding its multifaceted impact can empower users to make informed choices regarding its use in both recreational and medicinal contexts.
Potential Benefits and Risks of THC Consumption
Consumption of THC can lead to a myriad of effects, some positive, others not so much. Many users experience enhanced sensory perception, relaxation, and even relief from conditions such as chronic pain and anxiety. These benefits have transformed the landscape of therapeutic cannabis, with THC being recognized for its potential to alleviate symptoms of various medical conditions. However, it’s imperative to approach THC with caution. Possible adverse effects include impaired memory, anxiety, and an altered sense of time, which can impact daily activities and decision-making processes.
Another factor to consider is the legality and the varying quality of THC products available in the market. Different strains can offer diverse benefits and risks, as potency and individual reactions vary significantly. Regular use can lead to tolerance, meaning higher doses may be required to achieve the same effects, which raises the risk of dependence. Here’s a simple table summarizing some of the potential benefits and risks:
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Relief from chronic pain | Impaired memory |
| Reduced anxiety | Increased heart rate |
| Enhanced creativity | Possible addiction |
| Improved sleep quality | Altered perception of time |
Guidelines for Responsible Use and Further Research Recommendations
Responsible use of THC requires an understanding of its effects and the legal implications surrounding its consumption. Individuals should be informed about their local laws and regulations regarding THC, as legality can vary significantly from one region to another. Additionally, consider the following practices to promote safe usage:
- Start low, go slow: Initiate consumption with a low dose to gauge individual tolerance.
- Stay informed: Keep up with credible sources regarding the effects and potential risks associated with THC.
- Avoid impaired activities: Do not operate vehicles or engage in high-risk activities while under the influence.
Further research is essential to deepen our understanding of THC’s pharmacological properties and long-term effects. Scholars and institutions are encouraged to explore the following areas:
| Research Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Medicinal Uses | Investigate THC’s efficacy in treating chronic pain, anxiety, and other conditions. |
| Psychological Effects | Study how THC affects mental health and cognitive function over time. |
| Long-term Impact | Examine the consequences of regular THC use on physical and mental health. |
Q&A
Q&A: Is THC a Chemical?
Q1: What does THC stand for?
A1: THC stands for tetrahydrocannabinol, which is a compound found in the Cannabis sativa plant. It’s one of the primary active ingredients responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with marijuana use.
Q2: Is THC a chemical?
A2: Yes, THC is indeed a chemical. To be precise, it is a cannabinoid, a type of chemical compound that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system. As a molecule, it has a distinct chemical structure and formula, which allows it to produce various effects in the body.
Q3: How does THC work within the body?
A3: THC works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and other parts of the body. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating many physiological processes, including mood, memory, pain sensation, and appetite. When THC binds to these receptors, it can alter neurotransmitter release, leading to the characteristic effects of feeling high.
Q4: Are all chemicals in cannabis like THC?
A4: Not all chemicals in cannabis are like THC. The plant contains a variety of cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes, each with its own unique effects and interactions. For instance, CBD (cannabidiol) is another prominent cannabinoid that does not produce a psychoactive effect like THC does. The interplay between these compounds creates what is known as the “entourage effect,” enhancing or modifying the overall effects of the plant.
Q5: Can THC be synthesized artificially?
A5: Yes, THC can be synthesized in a laboratory. Synthetic versions of THC, like Marinol, are available by prescription and are used to treat certain medical conditions such as nausea from chemotherapy or loss of appetite in HIV/AIDS patients. However, synthetic THC may not perfectly replicate the effects of naturally occurring THC due to differences in how the body processes these compounds.
Q6: Is THC considered safe?
A6: The safety of THC largely depends on the individual, the dosage, and the context of use. For some, it may provide therapeutic benefits, while others may experience adverse effects, such as anxiety or impaired cognitive function. Legal regulations surrounding THC also vary widely, influencing its availability and perceived safety.
Q7: How does the perception of THC as a chemical impact its legality?
A7: The perception of THC as a chemical has significantly influenced its legal status worldwide. As research continues to unveil its potential benefits and risks, public opinion and legislative actions have shifted, leading to increased legalization for both medicinal and recreational use in various regions. Understanding THC as a chemical entity rather than merely a product of a controversial plant can help foster more informed discussions and policies.
Q8: What’s next in the scientific exploration of THC?
A8: The scientific exploration of THC is rapidly evolving. Researchers are investigating its therapeutic potential, exploring its role in mental health treatment, chronic pain management, and even neuroprotection. As studies continue to unfold, we may learn more about the specific mechanisms of action, optimal usage, and the broader impact of THC and other cannabinoids on human health and society.
The Conclusion
while THC may often be viewed through the lens of its psychoactive properties and its association with cannabis culture, it is undeniably a complex chemical compound. Understanding THC as a chemical opens the door to exploring its broader implications—scientific, medical, and social. As research continues to evolve and our understanding deepens, THC may offer new insights into both the world of chemistry and the potential benefits of the cannabis plant. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned expert in the field, the exploration of THC invites us to reconsider its role within the tapestry of modern science and society. As we move forward, let us keep questioning, learning, and discovering the myriad ways in which chemistry shapes our lives.