Is Cannabis Psychoactive? Unraveling the Mysteries of a Controversial Plant
In a world where cannabis has evolved from a forbidden herb to a mainstream topic of conversation, the question of its psychoactivity often emerges like smoke in the air. With a history steeped in both stigma and intrigue, the psychoactive properties of cannabis have sparked debates ranging from recreational use to medicinal benefits. At the heart of these discussions lies a fascinating interplay of chemistry and culture, as well as the myriad ways in which this ancient plant interacts with the human body. As we dive into the depths of its compounds and effects, we aim to illuminate whether cannabis truly warrants its reputation as a psychoactive substance, or if it’s merely another chapter in the expanding narrative of this complex plant. Join us as we explore the science, the perceptions, and the truths that shape our understanding of cannabis in today’s society.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Psychoactivity in Cannabis
- The Role of Cannabinoids and Terpenes in Effects
- Exploring Individual Responses to Cannabis Use
- Safely Navigating Cannabis Consumption for Desired Effects
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Psychoactivity in Cannabis
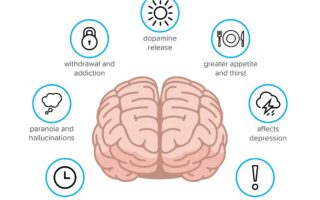
Psychoactivity in cannabis primarily stems from its interaction with the brain’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. The two main compounds that contribute to this psychoactive effect are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). While THC is renowned for producing the “high” commonly associated with cannabis use, CBD has gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects. It’s essential to differentiate between these compounds to understand the diverse experiences and effects cannabis can provide.
The psychoactive properties of cannabis can vary significantly based on several factors, including strain type, consumption method, and individual tolerance levels. The matrix of terpenes—aromatic compounds found in cannabis—also influences the psychological and physical response users have to specific strains. A few key factors include:
- Strain Type: Indicas may promote relaxation, while sativas are often associated with uplifting effects.
- Consumption Methods: Smoking, vaping, edibles, and oils can all yield different psychoactive experiences.
- Dosage: Higher doses of THC can intensify effects, while lower doses may lead to mild or no psychoactivity.
Understanding how these elements interact is vital for users seeking to navigate their cannabis experience safely and effectively. Below is a simplified overview of how different strains may affect individuals:
| Strain Type | Psychoactive Effects |
|---|---|
| Indica | Relaxation, Sedation |
| Sativa | Euphoria, Focus |
| Hybrid | Balanced Effects |
The Role of Cannabinoids and Terpenes in Effects
The intricate dance of cannabinoids and terpenes within the cannabis plant plays a pivotal role in shaping its effects on the human body and mind. Cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), interact with the endocannabinoid system, a complex network that regulates various physiological processes. THC is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with cannabis, inducing euphoria, altered perception, and increased appetite. In contrast, CBD has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic benefits without the mind-altering high, offering calming effects and relief from anxiety and inflammation. This unique balance of cannabinoids creates what is often referred to as the “entourage effect,” where the overall impact is greater when cannabinoids work synergistically rather than in isolation.
On the other hand, terpenes—the aromatic compounds found in cannabis—contribute not only to the plant’s fragrance but also enhance and modify its effects. These compounds can create diverse profiles that influence mood and sensation. For instance, myrcene, a common terpene in indica strains, is associated with sedative effects, while limonene offers uplifting and stress-relieving properties. Factors like strain selection, consumption method, and the individual’s unique physiology can lead to different experiences. Understanding this complex interaction between cannabinoids and terpenes is essential for anyone exploring the diverse effects of cannabis, creating a rich landscape that extends beyond mere psychoactivity to encompass therapeutic potential and personal well-being.
Exploring Individual Responses to Cannabis Use
Understanding how individuals respond to cannabis use requires a nuanced exploration of various factors that can influence their experiences. Biology, psychology, and environment all play critical roles in shaping how cannabis affects someone. Research has shown that individual genetics can significantly determine the endocannabinoid system’s efficiency, impacting whether a user feels euphoric or anxious after consumption. Furthermore, personal history—such as previous experiences with drugs—can also color one’s perception and reaction. Here are key factors affecting individual responses:
- Genetic Variations: Differences in genes may influence tolerance and sensitivity.
- Consumption Method: Smoking, vaping, or edibles deliver different effects.
- Dose: Larger doses can lead to heightened psychoactive experiences.
Moreover, the entourage effect of cannabis—the synergistic interaction of various compounds within the plant—can modulate the psychoactive experience. Strains rich in THC may produce stronger psychoactive effects, while those with significant CBD content tend to lessen them. Understanding the balance between these compounds provides insight into why two individuals using the same product may have vastly different reactions. To further illustrate, consider the following correlation:
| Strain Type | Average THC Content | Psychoactive Experience Level |
|---|---|---|
| Sativa | 15-25% | High |
| Indica | 10-20% | Medium |
| Hybrid | 12-22% | Variable |
Safely Navigating Cannabis Consumption for Desired Effects
Understanding the complexities of cannabis consumption is essential for achieving the desired effects and maintaining safety. The psychoactive properties of cannabis primarily stem from THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), which interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body. Here are some key considerations for those venturing into cannabis use:
- Start Low, Go Slow: Begin with a low dose of THC to gauge your sensitivity and reaction.
- Know Your Product: Research different strains and methods of consumption to find what suits your preferences.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help manage potential dry mouth and enhance your overall experience.
- Set the Scene: Choose a comfortable, familiar environment to enjoy your cannabis experience safely.
- Be Mindful of Interactions: Avoid mixing cannabis with alcohol or other substances to better assess its effects on you.
Monitoring your experience and adjusting as necessary can lead to a more tailored and enjoyable journey. Below is a simple comparison of various methods of consumption and their onset times:
| Method | Onset Time | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Inhalation (smoking, vaping) | 2-10 minutes | 1-3 hours |
| Edibles | 30-90 minutes | 4-6 hours |
| Tinctures | 15-45 minutes | 2-4 hours |
| Topicals | Varies | Local, ongoing relief |
Q&A
Q&A: Is Cannabis Psychoactive? Unraveling the Mystery
Q1: What does “psychoactive” mean in relation to substances like cannabis?
A: The term “psychoactive” refers to substances that affect the brain and alter mood, perception, behavior, or consciousness. In the context of cannabis, this means it can change the way a person thinks or feels by interacting with the brain’s chemistry.
Q2: What compounds in cannabis are responsible for its psychoactive effects?
A: The most well-known compound in cannabis associated with psychoactivity is THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). THC mimics the action of naturally occurring neurotransmitters in the brain, binding to cannabinoid receptors and producing effects such as euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and even increased appetite.
Q3: Are all strains of cannabis psychoactive?
A: Not all strains are created equal! While most strains of cannabis contain THC and are therefore considered psychoactive, some strains, particularly those bred to be high in CBD (cannabidiol), have very low THC levels. These low-THC strains may not produce significant psychoactive effects but can still offer other therapeutic benefits.
Q4: Can cannabis be psychoactive without causing a “high”?
A: Yes, it can! While THC is primarily responsible for the euphoric ”high,” other cannabinoids and compounds in cannabis may interact with the brain differently. CBD, for instance, may provide calming effects without the psychoactive kick. Users may experience anxiety reduction or pain relief without feeling intoxicated.
Q5: How does the method of consumption affect cannabis’s psychoactive effects?
A: The method of consumption plays a significant role! Smoking or vaping cannabis tends to produce quicker, more intense psychoactive effects compared to consuming edibles. Edibles, on the other hand, are metabolized and can lead to a delayed and prolonged experience, often resulting in a stronger effect overall.
Q6: Are there any factors that can influence how psychoactive cannabis is for an individual?
A: Absolutely! Factors such as an individual’s tolerance, genetic makeup, previous experiences with cannabis, and even the environment in which they consume it can all shape the psychoactive experience. As each person responds differently, what may be a mild effect for one could be intense for another.
Q7: Is it safe to say that cannabis is entirely psychoactive?
A: Not necessarily. While THC dominates the conversation about cannabis’s psychoactive properties, the presence of other cannabinoids, terpenes, and non-psychoactive variants complicates the picture. Thus, it’s crucial to consider the full spectrum of what cannabis offers rather than categorizing it solely as a psychoactive substance.
Q8: What is the takeaway regarding cannabis’s psychoactivity?
A: Cannabis is indeed a psychoactive plant, largely due to THC, but its effects are nuanced and varied. With diverse strains, varying consumption methods, and a multitude of compounds at play, the psychoactive experience can range widely. Understanding these distinctions helps users make informed choices about their consumption.
Final Thoughts
the question of whether cannabis is psychoactive reveals a tapestry of complexities woven into the fabric of this ancient plant. As we have explored, the compounds within cannabis—primarily THC—interact with the brain’s endocannabinoid system, leading to a diverse array of effects that can alter perception, mood, and cognition. While many may associate the term ’psychoactive’ solely with euphoric highs or altered states, the very essence of cannabis encompasses a broader spectrum of experiences, including therapeutic benefits that have gained recognition in both scientific and medicinal communities.
As research continues to uncover the multifaceted nature of cannabis, it’s crucial for us to approach the subject with nuance and an open mind. Whether one views it as a tool for healing, a recreational substance, or simply a part of cultural history, acknowledging the psychoactive nature of cannabis invites deeper conversations about its role in our lives and societies. As we move forward, let us embrace the ongoing dialogue, informed by science and grounded in experience, illuminating the path toward understanding this remarkable plant and its effects on the human psyche.