Does THC Make You High? Unveiling the Science Behind the Buzz
As the allure of cannabis continues to weave itself into the fabric of modern culture, one question remains at the forefront of the conversation: Does THC truly make you high? Tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is often heralded as the star player in the cannabis game, known for its psychoactive properties that have sparked curiosity, debate, and research. In this article, we journey beyond the surface-level understanding of THC’s effects, dissecting the science behind its interaction with our brain and body, while also exploring the myriad of experiences it can elicit. Whether you’re a seasoned user or a cautious newcomer, understanding the nuances of THC can illuminate not only its role in the world of cannabis but also its potential impact on health and wellness. Join us as we explore the complex relationship between THC and the state of being high, unraveling myths and highlighting the facts in this captivating exploration of cannabinoids.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Psychoactive Properties of THC
- The Science Behind THCs Effects on the Brain
- Factors Influencing the Intensity of the High
- Safe Consumption Practices for a Better Experience
- Q&A
- Concluding Remarks
Understanding the Psychoactive Properties of THC
The psychoactive effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are often a primary consideration for individuals curious about cannabis use. When consumed, THC primarily interacts with the endocannabinoid system, particularly binding to the CB1 receptors in the brain. This interaction triggers a myriad of sensations and cognitive alterations, leading to what many describe as a “high.” Individuals defining their experiences might highlight various effects, such as:
- Elevated mood
- Increased sensory perception
- Altered perception of time
- Enhanced creativity or focus
- Relaxation or euphoria
However, the intensity and nature of these effects can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including strain, dosage, method of consumption, and individual tolerance. For instance, sativa strains are generally known for their uplifting effects, while indica strains often induce sedative effects. Below is a brief comparison to illustrate how these factors might influence user experience:
| Strain Type | Common Effects |
|---|---|
| Sativa | Energetic, creative, uplifting |
| Indica | Relaxing, tranquil, calming |
| Hybrid | Balanced effects, varies widely |
The Science Behind THCs Effects on the Brain
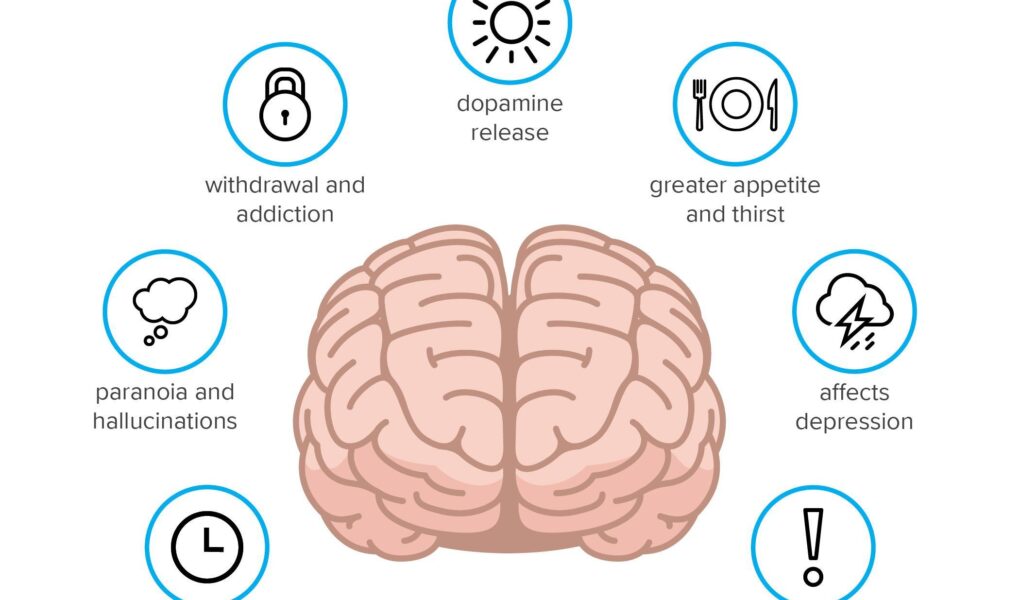
The interaction between THC and the brain is a complex dance that begins when THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, binds to specific receptors in the nervous system. These receptors, particularly the CB1 receptors found in areas of the brain associated with pleasure, memory, and cognition, play a pivotal role in the psychoactive effects of cannabis. When THC attaches to these sites, it can trigger various biochemical responses that alter neurotransmitter release, fundamentally transforming the user’s perception and experience. Some of the most significant effects include:
- Euphoria: A heightened sense of pleasure and well-being.
- Altered Time Perception: A distorted sense of how time is experienced.
- Heightened Sensory Perception: Enhanced appreciation of visual and auditory stimuli.
- Relaxation: A profound sense of calm and reduced anxiety.
Moreover, ongoing research continues to reveal how THC influences brain function on a molecular level. The compound can release dopamine, a neurotransmitter linked to the brain’s reward system, reinforcing the pleasure associated with THC use. Additionally, THC may also influence memory and learning by impacting the hippocampus, raising questions about its long-term effects. Here’s a brief overview of its impact on key brain areas:
| Brain Area | Effect of THC |
|---|---|
| Hippocampus | Memory formation interference |
| Amygdala | Emotional response enhancement |
| Cerebellum | Coordination and motor skills impairment |
Factors Influencing the Intensity of the High
The experience of being high from THC is influenced by a multitude of factors that can enhance or diminish its intensity. Some of these factors include:
- Individual Tolerance: Regular users may develop a tolerance to THC, necessitating higher amounts for the same effects.
- Method of Consumption: Different consumption methods, such as smoking, edibles, or oils, can affect the onset and overall intensity of the high.
- Strain Variation: Different cannabis strains have varying THC levels and profiles, which can produce diverse effects.
- Set and Setting: The user’s environment and mindset can greatly influence their experience, with comfort and visual stimuli playing key roles.
Additionally, there are physiological aspects that contribute to the strength of the high:
- Body Chemistry: Each person’s unique biology, including metabolism and endocannabinoid system balance, can alter the effect.
- Hydration Levels: Staying hydrated can affect how THC is metabolized, influencing its impact.
- Food Intake: Consuming THC on an empty stomach can lead to a quicker, more intense high.
| Factor | Influence on High |
|---|---|
| Strain THC Levels | Higher THC = Stronger Effects |
| Method of Use | Edibles may induce longer-lasting highs |
| Set & Setting | Positive environments enhance experiences |
Safe Consumption Practices for a Better Experience
To ensure a positive experience when consuming THC, it is vital to practice responsible and safe methods. Start by understanding your tolerance, as each individual reacts differently to THC. Experimenting with low doses can help gauge how your body responds. Consider the following tips for safer consumption:
- Choose Quality Products: Always opt for lab-tested cannabis products to avoid contaminants.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help mitigate potential side effects like dry mouth.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: Use a familiar and safe space for consumption, preferably with friends who share similar experiences.
- Avoid Mixing Substances: Steering clear of alcohol or other drugs can help maintain control of your experience.
Additionally, pay attention to the method of consumption as it can influence the effects. For instance, edibles may take longer to kick in but can lead to more intense experiences, while vaping or smoking often produces quicker, albeit shorter, effects. Below is a simple comparison:
| Consumption Method | Onset Time | Duration of Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking/Vaping | Immediate (minutes) | 1-3 hours |
| Edibles | 30-90 minutes | 4-8 hours |
By adhering to these safe consumption practices, you can foster a more enjoyable experience while exploring the effects of THC.
Q&A
Q&A: Does THC Make You High?
Q: What is THC?
A: THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the principal psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It’s responsible for the “high” that many users report, but it also has various therapeutic properties that scientists are beginning to understand.
Q: How does THC induce a high?
A: THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 receptors found in the brain. This interaction can lead to alterations in mood, perception, and consciousness, effectively producing the euphoric sensation commonly referred to as a “high.”
Q: Is the feeling of being high the same for everyone?
A: Not at all! The effect of THC can vary widely based on several factors, including an individual’s body chemistry, tolerance level, consumption method (smoking, edibles, oils), and the strain of cannabis used. For some, it may induce relaxation and euphoria, while for others, it might cause anxiety or paranoia.
Q: What factors can influence the intensity of the high?
A: Several factors play a role in the intensity of the high, including dosage, the method of consumption, the presence of other cannabinoids (like CBD), and individual biochemistry. Higher THC concentrations in a product typically lead to a stronger high, but personal tolerance and experience also significantly impact how one feels.
Q: Can you still experience benefits from THC without getting high?
A: Yes, many users find that certain strains or products contain lower levels of THC along with other cannabinoids like CBD. These can provide therapeutic effects without the overwhelming psychoactive experience. This has led to the development of various products aimed at those who seek relief from conditions like anxiety or chronic pain without the high.
Q: Are there any risks associated with THC use?
A: Like any substance, THC has potential risks. These can include impaired judgment, altered coordination, and increased heart rate. In some individuals, particularly those predisposed to mental health issues, THC can exacerbate symptoms or induce feelings of paranoia or anxiety. Responsible usage and understanding one’s limits are crucial.
Q: How does tolerance to THC develop?
A: Regular use of THC can lead to tolerance, where the body becomes accustomed to the compound, requiring larger amounts to achieve the same effects. It’s similar to how people may need to increase the dose of certain medications over time. A break from usage can help reduce tolerance levels.
Q: Is it possible to “overdose” on THC?
A: While it’s virtually impossible to fatally overdose on THC, consuming excessively concentrated or high amounts, especially via edibles, can lead to unpleasant experiences. Users might experience extreme anxiety, increased heart rate, and other distressing symptoms. It’s recommended to start low and go slow, particularly with edibles.
Q: Can you become addicted to THC?
A: There is potential for developing a dependency on THC, though it’s less common than substances like alcohol or opioids. Approximately 9% of users may develop a dependence, according to research. Those who start using cannabis at a young age or have a history of substance use disorders may be at higher risk.
Q: What’s the takeaway regarding THC and getting high?
A: THC indeed has the capacity to make users high due to its interaction with the brain’s receptors. However, the experience can differ greatly among individuals. It’s essential to approach THC mindfully, understanding both its effects and potential risks, while recognizing its therapeutic potential as well.
Concluding Remarks
In the intricate dance between chemistry and consciousness, THC emerges as a fascinating protagonist, captivating minds and altering perceptions with its psychoactive allure. As we have explored, the effects of THC are as varied as the individuals who partake in it, shaped by a tapestry of factors including dosage, method of consumption, and personal biochemistry. While it undeniably can make you feel high, the experience is subjective, blending relaxation, euphoria, and even occasional introspection.
As this dialogue around THC continues to evolve alongside changing social and legal landscapes, it’s essential to approach it with curiosity and respect. Whether you’re a seasoned consumer or merely an interested observer, understanding THC’s role in human experience encourages a broader conversation about wellness, moderation, and the complexities of our relationship with substances. As you journey forward, may your exploration be informed, insightful, and infused with a sense of wonder about the mind’s uncharted territories.