In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis culture, one acronym has emerged at the forefront of scientific discussion and recreational allure: THC. Short for tetrahydrocannabinol, this compound has captured the attention of enthusiasts and researchers alike, serving as both the infamous psychoactive element of marijuana and a focal point in the exploration of natural remedies. But what exactly is THC, and why does it hold such significance in the realms of medicine, law, and popular culture? This article delves into the intricate world of THC, unpacking its chemical composition, effects, and the implications of its legalization—illuminating a subject that continues to spark curiosity and debate across the globe. Join us as we define THC, unraveling its complexities and understanding its role in contemporary society.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of THC and Its Role in Cannabis
- Exploring the Therapeutic Benefits and Risks of THC Consumption
- Navigating the Legal Landscape Surrounding THC Use
- Guidelines for Responsible THC Consumption and Dosage
- Q&A
- In Retrospect
Understanding the Basics of THC and Its Role in Cannabis
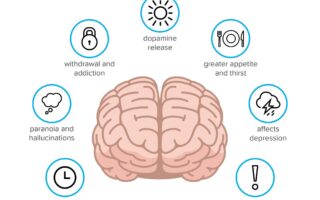
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as THC, is one of the principal active compounds found in cannabis. This compound is predominantly responsible for the psychoactive effects that users experience, often referred to as the “high.” THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, specifically binding to CB1 receptors predominantly found in the brain. Through this connection, it can influence a myriad of functions, including mood, memory, appetite, and pain perception. This psychoactive property can create both therapeutic and recreational experiences, making it a unique and multi-faceted compound in the cannabis plant.
Aside from its psychoactive role, THC also carries various potential therapeutic benefits. Research highlights that it can be beneficial in treating conditions such as chronic pain, nausea (particularly in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy), and muscle spasms related to multiple sclerosis. These medicinal aspects have spurred significant interest in THC as a treatment option, leading to an increase in both medical and recreational cannabis use. To further understand its role, here’s a concise table showcasing THC’s common effects and therapeutic applications:
| Effect | Application |
|---|---|
| Psychoactive High | Recreational Use |
| Pain Relief | Chronic Pain Management |
| Appetite Stimulation | Weight Management |
| Anxiety Reduction | Stress Relief |
Exploring the Therapeutic Benefits and Risks of THC Consumption
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, affecting various physiological and cognitive processes. Many individuals report that THC can help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as chronic pain, insomnia, and anxiety. The therapeutic benefits often highlighted include:
- Relief from chronic pain: THC may reduce inflammation and alleviate pain sensations.
- Anxiety relief: Some users find that THC reduces feelings of anxiety and enhances mood.
- Improved sleep quality: It is commonly used to combat insomnia and promote better sleep.
However, the consumption of THC is not without risks. While it can be beneficial for some, it may also lead to unwanted side effects, particularly when consumed in high doses or by individuals with certain predispositions. Potential risks associated with THC use include:
- Psychotropic effects: The high from THC can lead to paranoia, anxiety, or altered perception.
- Dependency potential: Long-term use may lead to increased tolerance and dependence.
- Impaired cognitive function: THC can impair short-term memory and alter motor coordination.
Navigating the Legal Landscape Surrounding THC Use
As the tide of legalization sweeps across various states and countries, understanding the legal landscape surrounding THC use becomes increasingly essential. Various factors govern the status of THC, including local laws, federal regulations, and even cultural perceptions. The distinction between recreational and medicinal use often complicates this landscape, resulting in a patchwork of legal boundaries. Individuals exploring THC for therapeutic purposes must navigate regulations that not only address possession limits but also specify permissible forms of consumption, such as edibles, tinctures, or oils.
Moreover, staying informed about ongoing legislative changes is crucial, as laws can shift rapidly. Key points to consider include:
- Age Restrictions: Many jurisdictions impose minimum age requirements for THC use.
- Licensing for Sales: Only licensed dispensaries may legally sell THC products.
- Driving Laws: THC impairment laws can affect the legality of driving under its influence.
Understanding these dynamics enables users to make informed choices while staying compliant with the law. By keeping abreast of the shifting regulations, individuals can better advocate for their rights and responsibly enjoy the benefits of THC.
Guidelines for Responsible THC Consumption and Dosage
When exploring the world of THC consumption, it’s vital to approach it with care and mindfulness. Start by understanding your tolerance level, as this can vary greatly from person to person. Beginners are encouraged to begin with a low dosage, typically around 2.5 to 5 mg of THC, and gradually increase it as needed. This helps to prevent any adverse effects and allows your body to adjust to the substance. Additionally, consider the method of consumption, as edibles can have a delayed onset of effects compared to smoking or vaping, which can lead to accidental overconsumption. Always keep track of your dosage and the time elapsed since your last intake.
Creating a safe environment for your THC experience is equally important. Surround yourself with trustworthy companions who can support you during your journey. Keep the following guidelines in mind to enhance responsible consumption:
- Stay hydrated to mitigate potential dry mouth effects.
- Avoid consuming THC in risky situations, such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Know the laws in your area regarding THC use to ensure compliance.
For those interested in tracking their consumption habits, consider using a simple table to record effects:
| Dosage (mg) | Method of Consumption | Onset Time (min) | Duration (hrs) | Effects Noted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 | Edible | 90 | 4-6 | Relaxation |
| 5 | Vape | 5 | 2-3 | Elevation of Mood |
| 10 | Joint | 10 | 2-4 | Increased Appetite |
Q&A
Q: What does THC stand for?
A: THC stands for tetrahydrocannabinol, which is one of the primary psychoactive compounds found in cannabis. It’s the component responsible for producing the “high” that many associate with marijuana use.
Q: How does THC interact with the body?
A: THC interacts with the body by binding to specific receptors in the endocannabinoid system, particularly the CB1 receptors found in the brain and central nervous system. This interaction affects various bodily processes, including mood, memory, and pain perception, which explains THC’s diverse effects on emotions and physical sensations.
Q: Is THC the only compound in cannabis?
A: No, THC is just one of over a hundred cannabinoids present in cannabis. Other well-known compounds include CBD (cannabidiol), which does not have psychoactive properties and is often explored for its potential therapeutic benefits, and CBG (cannabigerol), which is thought to have different effects and benefits.
Q: What are the potential benefits of THC?
A: THC has been studied for various medicinal benefits. It may help alleviate chronic pain, stimulate appetite in patients undergoing treatments like chemotherapy, reduce nausea, and even play a role in managing certain neurological conditions. However, effects can vary widely among individuals.
Q: Are there any risks associated with THC consumption?
A: Yes, while THC can provide benefits, it also carries risks. Common side effects include increased heart rate, anxiety, impaired memory, and coordination issues. Long-term or excessive use can contribute to the development of cannabis use disorder and may impact mental health, especially in those with predisposed conditions.
Q: How is THC consumed?
A: THC can be consumed in various forms, including smoking dried cannabis flowers, vaping oils, or using edibles infused with THC. Each method has a different onset time and duration of effects, prompting users to choose based on their preferences and desired experience.
Q: Is THC legal everywhere?
A: No, the legality of THC varies by region. In some places, it is fully legal for recreational and medicinal use, while in others it remains prohibited or restricted to medical use only. It’s essential to understand local laws regarding THC to avoid legal issues.
Q: What should someone consider before using THC?
A: Before using THC, individuals should consider their personal health history, current medications, and the context in which they plan to use it. Speaking with a healthcare provider can help identify any potential risks and ensure a safe experience, especially for those with mental health conditions or a history of substance use.
Q: What is the future of THC research?
A: The future of THC research is promising as attitudes towards cannabis continue to shift. Increased legalization and acceptance may lead to more studies exploring its potential benefits and risks, paving the way for new therapies and a better understanding of its effects on the human body.
In Retrospect
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of THC, it’s clear that this compound is far more than just a component of cannabis. With its complex chemistry, varying effects, and potential therapeutic benefits, THC remains a subject of fascination for scientists, medical professionals, and enthusiasts alike. Whether you’re seeking to understand its implications for health and wellbeing or simply curious about its cultural significance, THC invites a deeper understanding beyond the surface. As research continues and societal perceptions evolve, the journey to define THC is ongoing, promising new insights and a broader understanding of how this compound interacts with our bodies and minds. The world of THC is not just about highs and lows; it’s about discovery, understanding, and the nuances of human experience. So, as you venture forward, whether in curiosity or inquiry, keep in mind that every question leads to new possibilities.