In the ever-evolving landscape of wellness and agriculture, cannabinoids have emerged as a focal point of intrigue and innovation. These unique chemical compounds, primarily found in the cannabis plant, hold the key to unlocking a myriad of potential therapeutic benefits. Yet, the question remains: what exactly are cannabinoids? As scientific research continues to unveil their complexities and effects on the human body, from pain relief to anxiety management, understanding cannabinoids has never been more crucial. In this exploration, we will define cannabinoids, delve into their various types, and examine their significance in both medicinal and recreational realms. Join us on a journey through the fascinating world of cannabinoids, where science meets nature and possibilities abound.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Cannabinoids: A Comprehensive Overview
- The Endocannabinoid System: How Cannabinoids Interact with the Body
- Types of Cannabinoids: Essential Differences and Unique Benefits
- Navigating Cannabinoid Use: Recommendations for Safe and Effective Application
- Q&A
- To Conclude
Understanding Cannabinoids: A Comprehensive Overview
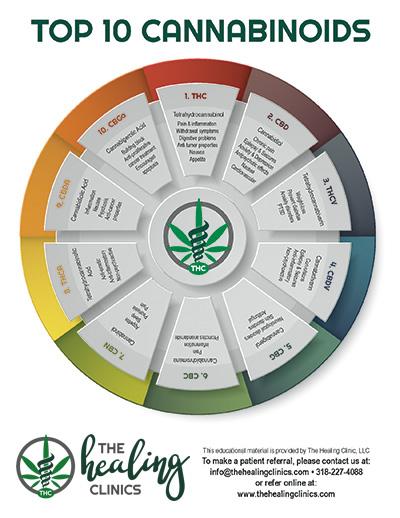
Cannabinoids are organic compounds that interact with the endocannabinoid system in the body, which plays a vital role in the regulation of various physiological processes. Found predominantly in the cannabis plant, these compounds can elicit a variety of effects on mood, appetite, pain sensation, and memory. The most well-known cannabinoids include tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), each offering distinct properties and potential health benefits. While THC is famous for its psychoactive effects, CBD has gained popularity for its therapeutic advantages without the high commonly associated with cannabis.
Beyond THC and CBD, there are over 100 other cannabinoids that contribute to the plant’s complex chemical profile. Some notable ones include cannabinol (CBN), known for its potential sedative effects, and cannabigerol (CBG), often touted for its potential neuroprotective properties. The interaction between cannabinoids and the body is a nuanced dance, influenced by factors like dosage, the method of consumption, and individual biochemistry. Understanding these unique compounds not only opens the door to potential therapeutic applications but also encourages a deeper appreciation for the natural world around us.
| Cannabinoid | Effects |
|---|---|
| THC | Psychoactive, euphoria, appetite stimulation |
| CBD | Anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory, non-psychoactive |
| CBN | Potential sedative, promotes sleep |
| CBG | Neuroprotective, potential anti-inflammatory |
The Endocannabinoid System: How Cannabinoids Interact with the Body
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis by interacting with naturally occurring compounds known as cannabinoids. These cannabinoids can either be phyto-cannabinoids, derived from the cannabis plant, or endogenous cannabinoids, which are produced within the body. When cannabinoids bind to the specific receptors in the ECS, they initiate a series of physiological changes that affect various bodily functions, including mood, pain sensation, immune response, and sleep patterns. The two primary types of receptors in the ECS are CB1 and CB2, predominantly located in the brain and immune system, respectively. Through their interactions, cannabinoids can trigger diverse effects by modulating neurotransmitter release, ultimately influencing bodily sensations and processes.
Understanding how cannabinoids work begins with recognizing their ability to mimic specific endocannabinoids like anandamide. This creates a complex dialogue between cannabinoids and the ECS, enabling therapeutic benefits that can be harnessed for conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation. Here are some key roles cannabinoids play in the body:
- Modulation of pain perception
- Regulation of mood and emotional responses
- Enhancement of appetite and digestive processes
- Support of immune function and inflammation reduction
the intricate relationship between cannabinoids and the ECS highlights their importance in both health and wellness, paving the way for emerging therapies and applications in medical science.
Types of Cannabinoids: Essential Differences and Unique Benefits
Cannabinoids, the remarkable compounds found in the cannabis plant, exhibit a fascinating variety of types, each with its distinct effects and benefits. Among the most well-known cannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). While THC is renowned for its psychoactive properties, causing the “high” associated with marijuana use, CBD presents a non-psychoactive alternative that offers therapeutic benefits without the euphoric effects. These compounds interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, influencing numerous physiological processes such as mood, pain regulation, and immune response.
In addition to THC and CBD, there are other cannabinoids that deserve attention for their unique attributes. Some lesser-known cannabinoids include CBG (cannabigerol) and CBN (cannabinol), which are gaining popularity for their potential health benefits. Here’s a brief overview of these cannabinoids:
| Cannabinoid | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| CBG | Potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. |
| CBN | May promote sleep and help with anxiety relief. |
| THCV | Could suppress appetite and assist in weight management. |
| CBC | May have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. |
Navigating Cannabinoid Use: Recommendations for Safe and Effective Application
As interest in cannabinoid use continues to surge, it’s essential to approach their application with careful consideration and informed choices. Understanding the various types of cannabinoids is critical, as they impart distinct effects on the body and mind. When utilizing cannabinoids, one should be aware of key factors to ensure a safe experience, including:
- Potency – Start with lower doses to gauge individual reactions, especially for newcomers.
- Source Legitimacy – Only select products from reputable manufacturers with third-party lab testing.
- Legal Compliance – Stay informed about local laws surrounding cannabinoid use to avoid legal issues.
- Strain Variances – Different strains may offer varying therapeutic benefits; consider personal wellness goals.
- Health Interactions – Consult healthcare professionals if you have existing health conditions or are on medication.
When employing cannabinoids, it’s also vital to employ proper delivery methods to maximize efficacy. Various forms are available, each with unique absorption rates and duration of effects. A comparison of popular methods includes:
| Delivery Method | Onset Time | Duration of Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking/Vaping | Instant | 1-3 hours |
| Edibles | 30-90 minutes | 4-6 hours |
| Tinctures | 15-45 minutes | 2-4 hours |
| Creams/Oils | Variable | 2-8 hours |
By being mindful of these considerations and tailoring cannabinoid use to individual preferences and needs, users can navigate this fascinating landscape responsibly and effectively.
Q&A
Q&A: Exploring the World of Cannabinoids
Q1: What are cannabinoids?
A1: Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. These compounds can be found in cannabis plants, such as marijuana and hemp, but can also be synthesized in laboratories. Essentially, cannabinoids can be thought of as nature’s way of communicating with our body’s receptors to promote balance and harmony.
Q2: How many types of cannabinoids are there?
A2: Cannabinoids can be classified into three main categories: phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids. Phytocannabinoids are those derived from the cannabis plant, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) being the most well-known. Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds produced by our bodies, and there are over a hundred identified in the cannabis plant, with ongoing research uncovering more. Meanwhile, synthetic cannabinoids are created in labs and can mimic the effects of their natural counterparts.
Q3: What are the most common cannabinoids and what do they do?
A3: The two most widely recognized cannabinoids are THC and CBD. THC is known for its psychoactive properties, producing the “high” typically associated with marijuana consumption. In contrast, CBD has gained popularity for its potential therapeutic benefits without psychoactive effects, often used for anxiety, pain relief, and inflammation. Other cannabinoids, such as CBG (cannabigerol) and CBN (cannabinol), are also under investigation for their unique effects and potential health benefits.
Q4: How do cannabinoids interact with the body?
A4: Cannabinoids interact with the body primarily through the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which consists of receptors (CB1 and CB2), endocannabinoids produced by the body, and enzymes. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they can help modulate various functions, including mood regulation, pain perception, immune response, and appetite. This interaction is what makes cannabinoids potentially beneficial in various medical and therapeutic contexts.
Q5: Are cannabinoids safe for everyone?
A5: The safety profile of cannabinoids varies widely depending on factors such as individual health conditions, dosages, and specific cannabinoid types. While many people report positive effects, some may experience side effects, particularly with THC, which can include anxiety or paranoia. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before integrating cannabinoids into your wellness routine, especially for individuals with pre-existing health concerns or those taking other medications.
Q6: What is the future of cannabinoid research?
A6: The future of cannabinoid research looks promising as interest in their therapeutic potential continues to grow. Studies are increasingly exploring their applications in treating conditions such as epilepsy, chronic pain, and even certain mental health issues. With ongoing advances in science and technology, we can expect to uncover more about how cannabinoids work, leading to better-informed health choices and potentially new cannabinoid-derived therapies.
Q7: In what forms can cannabinoids be consumed?
A7: Cannabinoids can be consumed in various forms, including oils, tinctures, capsules, edibles, and topical applications. Each method offers unique advantages, such as the quick onset of effects with vaping versus the long-lasting relief of edibles. The choice depends on individual preferences, desired effects, and the specific cannabinoids being used.
cannabinoids represent a fascinating and complex area of study with widespread implications for health and wellness. As our understanding deepens, these compounds hold the potential to revolutionize various aspects of medicine and lifestyle.
To Conclude
cannabinoids are fascinating compounds that play a pivotal role in the intricate tapestry of human health and wellness. Whether they are derived from the cannabis plant or synthesized in a laboratory, these chemical compounds interact with our endocannabinoid system in ways that continue to inspire research and open new avenues for therapeutic applications. As our understanding of cannabinoids deepens, so too does the potential for their use in addressing a range of medical conditions. With ongoing studies and evolving legal landscapes, the future may hold even more promise for these remarkable substances. As you continue to explore the world of cannabinoids, remember that knowledge is key, and staying informed will empower you to navigate the complexities and possibilities that lie ahead. Thank you for joining us on this enlightening journey into the realm of cannabinoids.