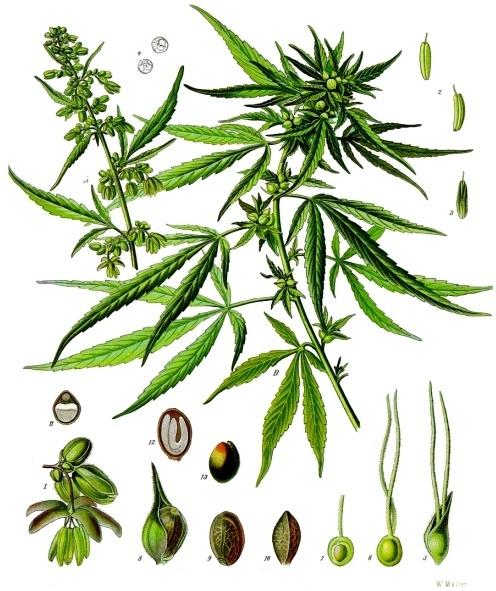
Title: The Green Frontier: Unveiling Cannabis Sativa Industrial Hemp
As the world increasingly turns its gaze towards sustainable solutions and eco-friendly practices, a familiar yet often misunderstood plant emerges as a beacon of potential: Cannabis sativa, specifically its industrial hemp variety. Often overshadowed by its more infamous cousin, marijuana, industrial hemp stands tall as a versatile powerhouse, capable of transforming industries and contributing to a greener future. With its rich history spanning thousands of years and a diverse range of applications—from textiles and building materials to bioplastics and biofuels—cannabis sativa industrial hemp offers a unique opportunity to rethink our relationship with nature. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of industrial hemp, exploring its properties, benefits, and the pivotal role it may play in shaping sustainable practices for generations to come. Join us on this journey to discover how this remarkable plant is redefining possibilities and paving the way for a more resilient planet.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Versatility of Cannabis Sativa Industrial Hemp
- Environmental Benefits of Hemp Cultivation
- Economic Potential: Fostering Sustainable Industries
- Navigating Regulations and Best Practices for Hemp Producers
- Q&A
- Closing Remarks
Exploring the Versatility of Cannabis Sativa Industrial Hemp
The fascinating nature of Cannabis Sativa industrial hemp reveals its adaptability across various sectors, making it a valuable asset in today’s market. Unlike its psychoactive cousin, industrial hemp boasts a high fiber and low THC content, making it suitable for a range of applications. This fibrous wonder is primarily utilized in the production of various materials, such as:
- Textiles: Durable clothing and eco-friendly fabrics.
- Construction: Hempcrete and insulation materials.
- Food Products: Nutritional seeds and oil.
Moreover, the versatility of this plant extends into sustainability as hemp requires minimal resources to thrive, making it a champion for eco-conscious practices. Its potential in bioremediation and carbon sequestration is notable, as it can absorb toxins from the soil, improving land health while simultaneously capturing carbon dioxide. Here’s a quick look at the environmental benefits of industrial hemp:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Health | Improves soil quality through deep roots. |
| Low Water Usage | Requires significantly less water than cotton. |
| Carbon Absorption | Absorbs more CO2 per hectare than trees. |
Environmental Benefits of Hemp Cultivation
The cultivation of *Cannabis sativa*, particularly in its industrial hemp form, offers a plethora of environmental advantages that contribute to a more sustainable future. Hemp is known for its rapid growth, often reaching full maturity in just 90 days, which means it can effectively sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This plant also requires significantly less water compared to many traditional crops. The deep-root system of hemp not only prevents soil erosion but also improves soil quality by breaking up compacted soil layers and enhancing nutrient retention. This leads to healthier ecosystems and boosts biodiversity.
Furthermore, industrial hemp plays a vital role in reducing the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers. Its natural resistance to pests and diseases means that farmers can cultivate hemp with minimal chemical inputs. Additionally, the vast array of products derived from hemp, such as biodegradable plastics, textiles, and building materials, offers an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based products. The following table summarizes the key environmental benefits:
| Environmental Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Carbon Sequestration | Absorbs significant amounts of CO2 due to rapid growth. |
| Water Conservation | Requires less water compared to conventional crops. |
| Soil Health | Enhances soil quality and prevents erosion. |
| Reduced Chemicals | Minimizes the need for pesticides and fertilizers. |
| Eco-friendly Products | Provides sustainable alternatives to plastic and other materials. |
Economic Potential: Fostering Sustainable Industries
The resurgence of cannabis sativa industrial hemp presents an incredible opportunity for the development of sustainable industries that could significantly impact our economy and environment. With its versatility, industrial hemp can be transformed into a myriad of products, ranging from textiles and biodegradable plastics to construction materials and biofuels. This plant, requiring minimal water and no pesticides, is ideal for eco-friendly manufacturing. The economic potential is immense, as cultivating hemp not only supports local farmers but also creates jobs across various sectors, thus revitalizing rural economies.
Incorporating hemp into mainstream industries can lead to a decrease in reliance on traditional resource-intensive materials, fostering a circular economy. Here are some areas particularly ripe for innovation:
- Textiles: Hemp fibers are durable and biodegradable, offering a sustainable alternative to synthetic fabrics.
- Construction: Hempcrete and insulation materials can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of building projects.
- Bioplastics: Developing bio-based plastics from hemp can curb plastic pollution.
To illustrate the diverse applications, consider the following table summarizing industrial hemp products and their benefits:
| Product | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hempcrete | Lightweight, excellent insulation, and carbon-negative |
| Hemp Oil | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, used in health products |
| Biodegradable Plastics | Reduces landfill waste and oil dependency |
Navigating Regulations and Best Practices for Hemp Producers
Hemp producers must stay vigilant in understanding and adhering to the complex web of regulations that govern the cultivation, processing, and distribution of industrial hemp. As the market landscape evolves, so too do the legal frameworks across different regions. It is essential for growers to keep track of their local and federal regulations, which often include:
- Licensing Requirements: Various states have specific licensing processes that must be completed prior to planting.
- THC Limits: Industrial hemp must legally contain less than 0.3% THC, necessitating regular testing to ensure compliance.
- Labeling Standards: Accurate labeling is vital, particularly if products are to be marketed for consumer use.
- Transportation Guidelines: Understanding the policies related to transport can prevent unlawful seizures and penalties.
In addition to regulatory compliance, producers can enhance their success and sustainability through best practices. Implementing environmentally friendly cultivation techniques not only boosts crop yield but also promotes soil health. Consider these best practices:
- Soil Testing: Regularly testing soil can provide insights into nutrient levels, aiding in informed fertilization practices.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating hemp with other crops can enhance soil fertility and reduce pest pressure.
- Water Management: Efficient irrigation practices are key to resource conservation while boosting plant health.
- Integrated Pest Management: Employing biological controls can minimize the use of chemical pesticides, promoting a healthier ecosystem.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Testing | Assess nutrient needs for optimal hemp growth. |
| Crop Rotation | Enhances soil health and pest management. |
| Water Management | Conserves water and ensures plant vitality. |
| Pest Management | Focuses on sustainable practices to counter pests. |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Cannabis Sativa Industrial Hemp
Q1: What is Cannabis Sativa industrial hemp?
A1: Cannabis Sativa industrial hemp is a versatile strain of the Cannabis sativa plant, specifically cultivated for industrial purposes. Unlike its psychoactive cousin, marijuana, hemp is defined by its low THC content (less than 0.3%) and high cannabidiol (CBD) levels. This unique composition allows hemp to be used in a wide array of products, including textiles, biofuels, paper, and construction materials.
Q2: How is industrial hemp different from marijuana?
A2: The primary difference lies in their chemical compositions. While both plants belong to the same species, industrial hemp is bred to produce minimal THC, the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana. In contrast, marijuana strains are specifically developed to maximize THC levels for recreational or medicinal use. This clear distinction is crucial for regulatory purposes and ensures that industrial hemp can be grown legally in many regions.
Q3: What are the environmental benefits of cultivating industrial hemp?
A3: Cultivating industrial hemp offers numerous environmental advantages. It grows quickly and requires minimal agricultural inputs, such as pesticides and herbicides. Hemp plants have deep roots that improve soil structure and prevent erosion, while also sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Furthermore, hemp can be used to detoxify the soil by absorbing heavy metals and pollutants, making it an environmentally friendly crop choice.
Q4: In what products can we find industrial hemp used?
A4: The applications of industrial hemp are diverse and expanding. This remarkable plant can be transformed into biodegradable plastics, sustainable building materials, textiles, food products (like hemp seeds and oil), biofuels, and health supplements. Furthermore, it plays a role in the cosmetics industry and is increasingly featured in health food products for its nutritional benefits.
Q5: Is industrial hemp legal to grow everywhere?
A5: The legality of growing industrial hemp varies by country and region. In the United States, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized the cultivation of industrial hemp with less than 0.3% THC on a federal level. However, states may have their own specific regulations regarding licensing and cultivation practices. Globally, many countries have also recognized the potential of industrial hemp and are moving towards more lenient legislation for its growth and production.
Q6: What are the economic impacts of industrial hemp cultivation?
A6: The economic potential of industrial hemp is considerable. As demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products grows, hemp offers new business avenues for farmers, manufacturers, and entrepreneurs. By diversifying agricultural practices, hemp farming can contribute to rural economic development, create jobs, and stimulate local economies. Many businesses are eager to explore the potential of hemp-based products, fostering innovation and investment in this burgeoning market.
Q7: Can hemp provide solutions for a sustainable future?
A7: Absolutely! Industrial hemp has the potential to contribute significantly to a sustainable future. Its ability to provide renewable resources across various industries reduces dependency on non-renewable materials and decreases environmental impact. As research and awareness about hemp’s benefits continue to grow, it may become a cornerstone in the transition to a more sustainable, circular economy, offering solutions to pressing global challenges like climate change and resource depletion.
Q8: How do I differentiate between hemp and marijuana products when shopping?
A8: When shopping, look for product labels that clearly indicate whether they are made from hemp or marijuana. Additionally, reliable brands will provide information about the THC content, typically showing that hemp-derived products contain less than 0.3% THC. Certified hemp products may also display seals or certifications that verify their compliance with legal standards. Always check the source of the product, as reputable companies will prioritize transparency and quality.
Closing Remarks
As we traverse the verdant landscape of cannabis sativa industrial hemp, it becomes clear that this versatile plant is far more than just a sibling to its psychoactive counterpart. From eco-friendly textiles to biodegradable plastics and nutritious seeds, industrial hemp stands as a testament to nature’s ingenuity, offering sustainable solutions in an increasingly resource-strapped world.
Its journey—once shrouded in stigma and misunderstanding—has blossomed into a robust narrative of innovation and resilience. As we cultivate awareness and understanding of its potential, we find ourselves at the precipice of a promising future, inviting exploration and dialogue around this remarkable crop.
In embracing cannabis sativa industrial hemp, we not only honor its rich heritage but also pave the way for a more sustainable and interconnected existence. Let us carry this knowledge forward, fostering a deeper appreciation for the role of hemp in our lives, and advocating for the continued exploration of its many possibilities. After all, in our quest for sustainability, sometimes the answers lie in nature’s own hands.