In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis research, one compound has begun to capture the attention of scientists, consumers, and enthusiasts alike: cannabis acid. Often overlooked in favor of its more famous relatives, THC and CBD, cannabis acid represents a fascinating area of study with the potential to reshape our understanding of the plant’s therapeutic properties. As the conversation surrounding cannabis transitions from prohibition to acceptance, the nuances of its chemical makeup come to the forefront, revealing a wealth of possibilities that lie within the raw, unprocessed state of the plant. In this exploration, we will delve into the intriguing world of cannabis acid, unraveling its defining characteristics, potential health benefits, and the implications it holds for the future of cannabis as both a medicinal powerhouse and a recreational staple. Join us as we illuminate this lesser-known aspect of cannabis, shedding light on its role in the broader context of this ancient yet modern botanical marvel.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Science Behind Cannabis Acids and Their Therapeutic Potential
- Unveiling the Unique Properties of Cannabinoid Acids: Beyond THC and CBD
- Maximizing Benefits: How to Incorporate Cannabis Acids into Wellness Routines
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Cannabis Acid Research and Use
- Q&A
- Closing Remarks
Exploring the Science Behind Cannabis Acids and Their Therapeutic Potential
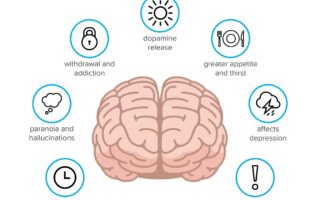
The world of cannabis is rich with a variety of compounds, among which cannabis acids stand out as a fascinating area of study. These compounds, primarily found in the raw, unheated plant, play a crucial role in the therapeutic effects associated with cannabis. Notably, cannabis acids such as THC-A and CBD-A are gaining recognition for their potential benefits in health and wellness. Researchers are beginning to uncover the distinct characteristics of these acids and their interactions within the endocannabinoid system, suggesting that their therapeutic potential may surpass even that of their decarboxylated counterparts.
One significant advantage of cannabis acids is their non-psychoactive nature, allowing users to experience relief without the intoxicating effects typically linked with THC. The potential healing properties of cannabis acids include:
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Neuroprotective properties
- Anti-nausea effects
This opens new avenues for treatment options, especially for patients who may be sensitive to THC or those seeking alternatives to traditional pharmaceuticals. As the scientific community continues to explore these compounds, we may soon witness a paradigm shift in how cannabis is perceived and utilized in modern medicine.
Unveiling the Unique Properties of Cannabinoid Acids: Beyond THC and CBD
The realm of cannabinoids is often dominated by well-known compounds like THC and CBD, but the spotlight is slowly shifting towards cannabinoid acids. These intriguing compounds, primarily known as THCA and CBDA, represent the raw, acidic forms of their more famous counterparts. While most cannabis enthusiasts are familiar with the decarboxylation process that converts cannabinoid acids into their neutral forms through heat, the unique properties of these acids merit a deeper exploration. These cannabinoid acids have shown potential therapeutic benefits, including:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Studies indicate that THCA may help reduce inflammation, offering potential relief for conditions like arthritis.
- Neuroprotective effects: Both THCA and CBDA have been linked to neuroprotection, potentially benefiting neurodegenerative disorders.
- Anti-nausea effects: Cannabinoid acids may also assist in alleviating nausea, making them a useful addition for chemotherapy patients.
Moreover, cannabinoid acids contain unique characteristics that differ significantly from their decarboxylated relatives. For instance, while THC is celebrated for its psychoactive effects, THCA does not produce a “high,” allowing users to explore the benefits without the associated intoxication. This aspect makes cannabinoid acids appealing for therapeutic use and research. A comparative overview of their properties illustrates these differences:
| Cannabinoid | Psychoactive | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | No | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-nausea |
| CBDA | No | Anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory, potential antibacterial properties |
| THC | Yes | Analgesic, appetite stimulation, euphoria |
| CBD | No | Anxiety reduction, anti-seizure, potential neuroprotective |
Maximizing Benefits: How to Incorporate Cannabis Acids into Wellness Routines
Incorporating cannabis acids into your wellness routine has the potential to unlock a new realm of benefits that traditional treatments may not provide. These naturally occurring compounds, such as cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), maintain the therapeutic properties of cannabis without the psychoactive effects. This makes them an attractive option for those looking to enhance their health regimen. To seamlessly integrate these acids, consider the following approaches:
- Raw Edibles: Incorporating raw cannabis leaves into smoothies or salads can help you capture the full spectrum of cannabinoids.
- Cold-Infused Oils: Use cannabis-infused olive or coconut oil in dressings or marinades, preserving the integrity of the acids.
- Capsules and Tinctures: Opt for capsules or tinctures specifically formulated with high concentrations of cannabis acids for easy consumption.
To better understand the unique benefits of these compounds, a quick comparison of cannabis acids and their decarboxylated forms can prove insightful:
| Cannabis Compound | Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| CBDA | Acid | Anti-inflammatory, potential anti-nausea |
| THCA | Acid | Neuroprotective, anti-emetic properties |
| CBD | Decarboxylated | Anxiety relief, pain management |
| THC | Decarboxylated | Psychoactive effects, appetite stimulation |
By mixing and matching these benefits in personalized wellness approaches, one can cultivate a balanced and holistic health routine that resonates with their individual needs. The versatility and potential of cannabis acids present exciting opportunities for longevity, vitality, and overall well-being.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Cannabis Acid Research and Use
The exploration of cannabis acids, such as cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the legal and regulatory landscape. Given the diverse regulations that govern cannabis across different jurisdictions, researchers and consumers must navigate a complex maze of compliance issues. State laws, federal regulations, and international treaties can vary significantly, impacting everything from cultivation to product distribution. For instance, while some regions have fully legalized cannabis use for recreational and medicinal purposes, others may still classify it strictly as a controlled substance. This discrepancy can pose challenges for researchers looking to conduct legitimate studies or for businesses aiming to market products derived from these compounds.
To foster a compliant and productive research environment, stakeholders should familiarize themselves with essential regulations, including the Controlled Substances Act, FDA guidelines, and local cannabis statutes. Key considerations include:
- Understanding the classification of cannabis under the federal controlled substances schedule.
- Ensuring accurate labeling and marketing of cannabis acid products to avoid misleading claims.
- Complying with safety regulations and ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects.
It’s vital for organizations engaged in cannabis acid research to maintain a thorough documentation process, ensuring transparency and readiness for audits or inspections. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) can provide necessary oversight for research activities, further safeguarding compliance with evolving regulations.
Q&A
Q&A on Cannabis Acid: Understanding the Potency Behind the Leaf
Q1: What exactly is cannabis acid?
A: Cannabis acid refers to the non-psychoactive precursor compounds in the cannabis plant. The three main types are tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). These acids are the raw forms of cannabinoids, and they undergo a process called decarboxylation when exposed to heat, transforming them into their active forms—THC, CBD, and CBG, respectively.
Q2: How are cannabis acids produced?
A: Cannabis acids are produced through the natural biosynthetic processes within the cannabis plant. As the plant matures, specialized glandular structures, known as trichomes, contain cannabinoid synthase enzymes that catalyze the formation of these acidic compounds from olivetolic acid and geranyl pyrophosphate.
Q3: What benefits do cannabis acids offer?
A: While research is still in its nascent stage, preliminary studies suggest that cannabis acids may hold a range of therapeutic benefits. For instance, THCA has shown promise in anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, while CBDA may assist in nausea reduction. These compounds offer an array of potential health benefits without the intoxicating effects associated with their decarboxylated counterparts.
Q4: How do cannabis acids differ from their activated forms?
A: The primary difference lies in their effects and potency. Cannabis acids are non-psychoactive; they do not produce a “high” like THC. When cannabis is heated through smoking, vaping, or cooking, the THC-A and CBD-A transform into THC and CBD, respectively. This decarboxylation process activates their potential therapeutic effects, leading to different applications in medical and recreational use.
Q5: Can cannabis acids be consumed directly?
A: Yes, cannabis acids can be consumed directly, particularly in raw or juiced forms of cannabis. Some users blend raw cannabis leaves into smoothies or salads, taking advantage of the potential health benefits of the acids without the psychoactive side effects. However, these methods require careful handling to ensure that the plant material is fresh and free of contaminants.
Q6: Are there any side effects associated with cannabis acids?
A: While cannabis acids are generally considered safe and non-psychoactive, individual responses can vary. Some people may experience mild side effects like digestive discomfort or allergy-like symptoms. As research continues, it’s crucial for users to consult healthcare professionals, especially those with underlying health conditions or who are pregnant.
Q7: What is the future of cannabis acid research?
A: The future of cannabis acid research looks promising. As interest in cannabinoids continues to grow, scientists are increasingly exploring their unique properties and potential applications. Continued exploration may unveil new therapeutic uses, inform cultivation practices, and contribute to a deeper understanding of the cannabis plant’s full spectrum of benefits.
This creative Q&A format aims to offer informative insights into cannabis acids while maintaining a neutral tone. Each question guides the reader toward a better understanding of this fascinating aspect of cannabis.
Closing Remarks
As we draw our exploration of cannabis acid to a close, it’s evident that this fascinating compound is more than just an offshoot of the cannabis plant; it embodies the potential for innovation in both medicine and holistic practices. The journey from cannabinoid acids to their activated counterparts opens a dialogue about the nuanced intricacies of this complex botanical world. As research expands and our understanding deepens, cannabis acid may well become a pivotal player in the ongoing narrative of cannabis science. Whether you’re a seasoned enthusiast or a curious newcomer, there’s no denying that the story of cannabis acid is just beginning. So, let’s keep our minds open and our questions ready as we await the next chapter in this ever-evolving tale.