In a world where the boundaries of wellness and healing are continually being redefined, cannabinoids have emerged from the shadows of a once-stigmatized plant to take center stage in the scientific discussion surrounding holistic health. These unique compounds, predominantly derived from the cannabis plant, have sparked a surge of interest among researchers, healthcare professionals, and wellness enthusiasts alike. As we delve into the intricate tapestry of cannabinoids, we invite you to explore their multifaceted effects on the human body and mind. From potential therapeutic benefits to the nuances of their interactions within our endocannabinoid system, this article aims to illuminate the captivating journey of cannabinoids in the pursuit of understanding their true impact on our well-being. Join us as we unravel the science, the myths, and the emerging realities of these powerful compounds that could redefine how we perceive health and healing in the modern era.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Unique Properties of Cannabinoids
- Exploring Therapeutic Benefits and Potential Risks
- Navigating the Interactive Effects with Other Compounds
- Practical Tips for Safe and Effective Usage
- Q&A
- Wrapping Up
Understanding the Unique Properties of Cannabinoids
At the heart of cannabis are cannabinoids, a dynamic group of compounds known for their profound interactions with the human body. These chemical compounds resemble endogenous neurotransmitters, known as endocannabinoids, which play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis. The way cannabinoids affect the body can be classified into two main categories: psychoactive and non-psychoactive. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the most recognized psychoactive cannabinoid, producing euphoria and altering perception. In contrast, CBD (cannabidiol) boasts a multitude of therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects, attracting attention from medical communities and wellness advocates alike.
The unique properties of cannabinoids extend beyond their basic classifications, delving into their mechanisms of action within the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Some noteworthy aspects include:
- Affinity for Receptors: Cannabinoids bind primarily to CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing various physiological processes.
- Entourage Effect: The synergistic interaction between different cannabinoids and terpenes can enhance therapeutic efficacy.
- Variability in Effects: Individual responses to cannabinoids can differ based on factors like genetics, tolerance, and method of consumption.
Understanding these properties not only demystifies the complex nature of cannabinoids but also informs potential therapeutic applications. Research continues to unveil the possibility of leveraging cannabinoids for a variety of conditions, from chronic pain relief to anxiety management. The table below summarizes some key cannabinoids and their primary effects:
| Cannabinoid | Primary Effects |
|---|---|
| THC | Psychoactive effects, pain relief, appetite stimulation |
| CBD | Anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, seizure reduction |
| CBG | Potential neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory |
| CBN | Promotes sedation, mild anti-inflammatory |
Exploring Therapeutic Benefits and Potential Risks
The therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids have sparked interest in both the medical community and among casual users alike. Research suggests that cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC, may offer a range of potential health advantages, including:
- Pain relief: Many individuals report significant reductions in chronic pain, making cannabinoids an appealing alternative to traditional pain medications.
- Anxiety and stress reduction: Preliminary studies indicate that cannabinoids might help alleviate symptoms of anxiety disorders and promote a sense of calm.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Certain cannabinoids have shown promise in reducing inflammation, which could be beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
- Sleep aid: Cannabinoids may assist in improving sleep quality, making them attractive for those suffering from insomnia.
However, it’s vital to consider the potential risks associated with cannabinoid use. While many users experience positive effects, some may encounter adverse reactions. Notable concerns include:
- Altered mental state: THC, in particular, can induce psychoactive effects, which may not be suitable for everyone.
- Dependency issues: There is potential for developing a reliance on cannabis, particularly among frequent users of high-THC products.
- Drug interactions: Cannabinoids may interact with other medications, affecting their efficacy and safety.
- Legal uncertainties: The legal status of marijuana varies greatly by region, which can complicate access and usage.
Navigating the Interactive Effects with Other Compounds
Understanding the interactive effects between cannabinoids and other compounds is crucial for anyone exploring the full potential of cannabis. These interactions can significantly influence the overall experience, therapeutic benefits, and side effects one might encounter. Factors to consider include:
- Terpenes: These aromatic compounds found in cannabis and other plants may enhance or modify the effects of cannabinoids.
- Flavonoids: Known for their antioxidant properties, these compounds can also contribute to the entourage effect, complementing the actions of cannabinoids.
- Other Medications: Cannabinoids may interact with prescription drugs, amplifying or reducing their effects, which is critical for patient safety.
Research continues to illuminate how these interactions unfold, emphasizing the complexity of the cannabis experience. To illustrate this interplay, consider the following table that summarizes the effects of particular cannabinoids with selected terpenes:
| Cannabinoid | Terpene | Combined Effects |
|---|---|---|
| CBD | Limonene | Enhanced mood and stress relief |
| THC | Myrcene | Increased sedation and pain relief |
| CBG | Caryophyllene | Potential anti-inflammatory benefits |
Practical Tips for Safe and Effective Usage
When exploring the world of cannabinoids, it is essential to approach usage with care and mindfulness. Here are some practical tips to maximize safety and effectiveness:
- Start low and go slow: Begin with a small dose to gauge your body’s response before increasing the amount.
- Set the environment: Use cannabinoids in a comfortable and familiar setting to enhance your overall experience.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, as cannabinoids can sometimes cause dry mouth.
- Know your product: Research the specific strain or type of cannabinoid, including its THC and CBD content, to better understand its effects.
- Document your experience: Keeping a journal of your reactions and dosages can help you track what works best for you.
Understanding interactions with other substances can also enhance safety. Consider the following tips:
- Consult healthcare professionals: Discuss any current medications with a doctor to avoid adverse interactions.
- Avoid combining with alcohol: Consuming cannabinoids with alcohol can amplify effects and lead to undesirable outcomes.
- Educate yourself on legalities: Know the laws concerning cannabinoid use in your area to ensure compliance.
| Dosage | Effect | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 mg THC | Mild euphoria | Good starting point for novices |
| 5 mg THC | Intensified sensations | Monitor personal limits |
| 10 mg THC | Very strong effects | Experienced users only |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Cannabinoids’ Effects
Q1: What exactly are cannabinoids?
A1: Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant. They interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters that helps regulate a variety of physiological processes. While THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are the most well-known cannabinoids, there are over a hundred different types, each with its unique effects.
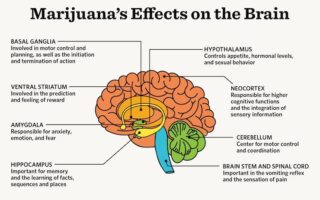
Q2: How do cannabinoids affect the body?
A2: Cannabinoids exert their effects by binding to specific receptors in the endocannabinoid system, primarily CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are predominantly found in the brain and central nervous system, influencing pain, mood, appetite, and memory. In contrast, CB2 receptors are mostly located in the immune system and peripheral tissues, playing a role in inflammation and immune response. This interaction can lead to a range of effects, from pain relief and reduced anxiety to appetite stimulation and potential modulation of immune functions.
Q3: Is THC the only cannabinoid that can produce a high?
A3: While THC is renowned for its psychoactive properties—creating the sensation of being “high”—it’s not the only compound that can influence mood or perception. Some lesser-known cannabinoids, such as THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin), can also impact mood but may do so in different ways, such as appetite suppression rather than enhancement. However, it is THC that is predominantly associated with psychoactive experiences.
Q4: What about CBD? How does it differ from THC?
A4: CBD is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that does not produce the “high” associated with THC. Research suggests that CBD can counteract some of THC’s psychoactive effects, even when the two are consumed together. CBD is often highlighted for its potential therapeutic benefits, which may include anxiety reduction, anti-inflammatory effects, and seizure control, without the intoxicating effects of THC.
Q5: Are there any side effects associated with cannabinoid use?
A5: Like any substance, cannabinoids can have side effects. THC, for instance, can lead to dry mouth, dizziness, increased heart rate, and impaired memory. CBD is generally well-tolerated, but high doses may cause fatigue or gastrointestinal issues. Because individual responses to cannabinoids can vary widely, it’s essential to approach use cautiously, particularly for those with underlying health conditions or who are taking other medications.
Q6: Can cannabinoids help with medical conditions?
A6: There is growing interest in the potential medical benefits of cannabinoids. Research indicates that THC can aid in pain management, particularly for chronic pain conditions, while CBD shows promise for issues like anxiety, epilepsy, and inflammation. However, while the potential is significant, much of the research is still ongoing, and clinical applications vary based on specific conditions and individual responses.
Q7: How does the method of consumption affect cannabinoid effects?
A7: The method of consumption plays a crucial role in how cannabinoids affect the body. Smoking or vaping provides immediate effects, as cannabinoids enter the bloodstream rapidly through the lungs. Edibles, on the other hand, are metabolized by the liver, resulting in delayed onset but potentially longer-lasting effects. Tinctures and topicals offer alternative options, with tinctures providing a sublingual method for quicker absorption and topicals targeting localized pain without psychoactive effects.
Q8: Will legal cannabis guarantee safe use of cannabinoids?
A8: While legal cannabis products undergo specific regulatory standards to ensure safety and quality, it doesn’t eliminate all risks associated with cannabinoid consumption. Variability in individual reactions, the presence of contaminants, and the complexity of cannabinoid interactions necessitate a cautious approach. Consumer education is vital, as is consulting healthcare professionals when considering cannabinoids for therapeutic use.
Q9: What future research is being done on cannabinoids?
A9: The field of cannabinoid research is rapidly expanding. Topics of focus include the therapeutic potential of lesser-known cannabinoids, understanding how different strains affect individual responses, and the long-term effects of cannabinoid use on both mental and physical health. Ongoing studies aim to unravel the complexities of how these compounds interact with the body to optimize their benefits while mitigating risks. As research progresses, our understanding of cannabinoids and their potential applications will continue to evolve.
This Q&A serves to shed light on cannabinoids and their myriad effects, inviting further exploration into a field brimming with potential yet anchored in the necessity for careful consideration and ongoing study.
Wrapping Up
As we journeyed through the intricate world of cannabinoids, it becomes clear that their effects are as diverse as the compounds themselves. From the soothing whispers of relaxation to the stimulating sparks of creativity, these natural substances interact with our bodies in ways that are both fascinating and complex. While research continues to unveil the myriad ways cannabinoids can influence our well-being, it’s essential for individuals to approach their use with an open mind and a discerning eye. As the conversation around cannabinoids evolves, informed choices will empower each of us to navigate this evolving landscape with confidence. whether for relief, exploration, or enhancement, the intersection of these compounds and human experience invites us to explore deeper, reflecting on how they fit within our own lives and communities. The story of cannabinoids is still being written, and each chapter promises to be as intriguing as the last.