Unlocking the Body’s Hidden Network: An Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System
In the intricate tapestry of human biology, there exists a seldom-discussed yet profoundly impactful system that orchestrates a delicate balance within our bodies. The endocannabinoid system (ECS), a master regulator of homeostasis, operates in the background, influencing everything from mood and stress response to pain perception and immune function. While cannabinoid-rich plants like cannabis have captured public attention for their medicinal properties, the ECS itself remains an enigmatic frontier in medical research and understanding. As we delve into the complexities of this remarkable network, we invite you on a journey to explore how the ECS interacts with our physiology, its potential therapeutic applications, and what its discovery means for the future of health and wellness. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of the endocannabinoid system, a hidden cornerstone of our well-being.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Endocannabinoid System: Understanding Its Role in Homeostasis
- The Biochemistry of Cannabinoids: How They Interact with the Endocannabinoid System
- Clinical Applications and Benefits: Insights into Therapeutic Uses of Cannabinoids
- Practical Recommendations for Supporting Endocannabinoid Function Through Lifestyle Choices
- Q&A
- The Way Forward
Exploring the Endocannabinoid System: Understanding Its Role in Homeostasis
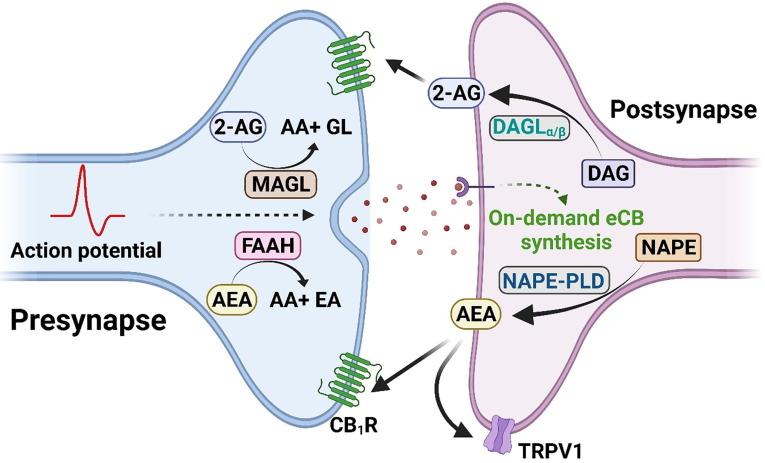
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is an intricate network of receptors, endocannabinoids, and metabolic enzymes that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. This remarkable system is comprised of two primary types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. These receptors are distributed widely throughout the nervous system, organs, and immune tissues, allowing them to regulate various physiological processes. The ECS helps to modulate a variety of functions including mood, appetite, pain sensation, immune response, and even memory. By responding to the body’s internal and external stimuli, it ensures that our bodily functions remain balanced and optimized for health.
- CB1 Receptors: Primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, influencing cognitive function and pain perception.
- CB2 Receptors: Located mainly in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells, associated with anti-inflammatory responses.
- Endocannabinoids: Naturally occurring compounds similar to cannabinoids in cannabis, crucial for signaling within the ECS.
- Enzymes: Involved in the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids, ensuring they function effectively.
Understanding the ECS opens up exciting avenues for research and therapeutic interventions. Emerging studies reveal its potential in treating a myriad of conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammatory disorders. Furthermore, the balance of the ECS can be affected by various lifestyle factors, including diet, stress, and exercise. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of this system, its implications for personalized health approaches and innovative treatments become increasingly significant. The interplay between the ECS and overall well-being underscores the importance of a holistic perspective on health management.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| CB1 Receptors | Regulate neurological function and pain |
| CB2 Receptors | Modulate immune system functions |
| Endocannabinoids | Facilitate communication within the ECS |
| Metabolic Enzymes | Control the lifecycle of endocannabinoids |
The Biochemistry of Cannabinoids: How They Interact with the Endocannabinoid System
The biochemistry of cannabinoids reveals a fascinating interplay with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a complex cell-signaling network integral to maintaining homeostasis. Cannabinoids, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), mimic the actions of naturally occurring endocannabinoids like anandamide and 2-AG, which are produced by the body. This mimicry allows cannabinoids to bind to specific cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2, located throughout the body, facilitating a myriad of physiological effects. Through this binding process, cannabinoids can modulate neurotransmitter release, influencing pain perception, mood regulation, immune responses, and even appetite.
Moreover, the interaction between cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system extends beyond simple binding. Different cannabinoids can activate or inhibit receptor activity in unique ways, leading to diverse therapeutic effects. For instance, whereas THC may produce psychoactive effects through strong binding to CB1 receptors in the brain, CBD has a more nuanced relationship with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, often acting as an antagonist at certain pathways to modulate the effects of THC. This differential interaction underscores the potential for tailored cannabinoid therapies that could maximize benefits while minimizing undesirable side effects, paving the way for future research in cannabinoid medicine.
| Cannabinoid | Receptor Interaction | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|
| THC | Strongly binds to CB1 | Psychoactive effects, pain relief |
| CBD | Modulates CB1/CB2 | Anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic |
| CBG | Emerging roles at CB1/CB2 | Potential neuroprotective, antibacterial |
| CBC | Weak CB2 interaction | Anti-inflammatory, pain relief |
Clinical Applications and Benefits: Insights into Therapeutic Uses of Cannabinoids
The therapeutic potential of cannabinoids has garnered significant interest in the medical community, leading to a deeper understanding of their interactions within the endocannabinoid system. These compounds exhibit a range of pharmacological effects that can be harnessed for various clinical applications. Some notable therapeutic uses include:
- Chronic Pain Management: Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are known for their analgesic properties, providing relief for patients with conditions like arthritis and neuropathic pain.
- Anti-Inflammation: CBD’s anti-inflammatory effects may benefit those with autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Anxiety and Mood Disorders: Preliminary studies suggest that cannabinoids can reduce anxiety levels, helping in the treatment of stress-related disorders.
- Cancer Symptom Relief: Cannabinoids can alleviate symptoms such as nausea and appetite loss associated with chemotherapy treatments.
Research continues to reveal the multifaceted benefits of cannabinoids, prompting healthcare professionals to explore their use across a variety of conditions. Recent clinical trials indicate promising results in areas like:
| Condition | Treatment Approach | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Sclerosis | Oral cannabinoid therapy | Reduced muscle spasms |
| PTSD | Inhalation of THC | Lessening of flashbacks |
| Epilepsy | High-CBD formulations | Decreased seizure frequency |
| Insomnia | Cannabinoid tinctures | Improved sleep quality |
Practical Recommendations for Supporting Endocannabinoid Function Through Lifestyle Choices
To nurture your endocannabinoid system, consider making mindful lifestyle choices that align with its regulation of balance and homeostasis. First and foremost, nutrition plays a crucial role. Incorporate a variety of whole foods rich in omega fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseed, and walnuts, which support endocannabinoid synthesis. Don’t overlook the benefits of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, such as berries, kale, and tomatoes, as they can help combat oxidative stress, potentially benefiting overall cannabinoid function. Additionally, maintaining a proper hydration level is vital; aim for at least eight glasses of water daily to facilitate the body’s metabolic processes.
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone for supporting endocannabinoid function. Engaging in moderate exercise, whether it’s jogging, swimming, or even yoga, can enhance the production of endocannabinoids like anandamide, often referred to as the “bliss molecule.” Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week. Lastly, consider the importance of stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or even spending time in nature, as chronic stress can disrupt endocannabinoid signaling. Creating a balanced life through these choices not only promotes a healthier physiology but can also enhance your overall well-being.
Q&A
Q&A on the Endocannabinoid System
Q1: What exactly is the endocannabinoid system (ECS)?
A1: Think of the endocannabinoid system as your body’s internal communication network, a bridge linking various systems to help maintain a balanced state known as homeostasis. Discovered in the early 1990s, the ECS is composed of endocannabinoids (the body’s own cannabinoids), cannabinoid receptors (like CB1 and CB2), and enzymes that help synthesize and break down these endocannabinoids.
Q2: What role does the ECS play in our health?
A2: The ECS is pivotal for regulating a multitude of functions in our body, including mood, memory, appetite, sleep, immune response, and pain sensation. It acts as a maestro, ensuring that these systems work harmoniously together to promote overall well-being.
Q3: How do endocannabinoids work?
A3: Endocannabinoids operate like key-and-lock mechanisms, binding to receptors scattered throughout the body. This binding initiates various responses that help mitigate any imbalances, responding to stresses or changes in our environment. For instance, if you’re feeling anxious, the ECS might release endocannabinoids to help produce a calming effect.
Q4: Can we influence our endocannabinoid system?
A4: Absolutely! Factors such as diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices play a significant role in the ECS’s health. Consuming omega-3 fatty acids, regular physical activity, and managing stress can all positively impact the ECS. Additionally, phytocannabinoids from plants, such as those found in hemp and cannabis, can also interact with the ECS, providing various therapeutic benefits.
Q5: Are there potential therapeutic applications for ECS research?
A5: Definitely! Researchers are exploring how the ECS might help in treating conditions like chronic pain, anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and even neurodegenerative diseases. By understanding the ECS more thoroughly, we may unlock new pathways for treatment that could alleviate symptoms without reliance on traditional pharmaceuticals.
Q6: Is there a downside to manipulating the endocannabinoid system?
A6: As with any system in the body, balance is key. Overstimulating or improperly influencing the ECS can lead to adverse effects. This can range from impairing cognitive functions to potential addiction issues with certain phytocannabinoids. Therefore, any approach to modifying ECS function should be done cautiously, ideally under professional guidance.
Q7: How can someone learn more about the endocannabinoid system?
A7: Knowledge is your ally! There are numerous reputable resources, including scientific journals, academic publications, and books focused specifically on the ECS. Engaging with healthcare professionals who specialize in this field can also provide clarity and insight into its complexities and implications for health and wellness.
Q8: What is the future of endocannabinoid system research?
A8: The future of ECS research is brimming with possibilities! As scientists continue to uncover its complexities, we may see groundbreaking advances in personalized medicine, targeted therapies, and a deeper understanding of how our lifestyle choices impact this essential system, all paving the way for innovative health solutions.
Concluding Thought: The endocannabinoid system, while still cloaked in mystery, promises to be a treasure trove for advancing our knowledge about health and well-being. As research progresses, who knows what fascinating revelations await?
The Way Forward
As we journey through the intricate landscape of the endocannabinoid system, it becomes clear that this remarkable network holds significant promise for understanding the complexities of human health and wellbeing. Like an unseen orchestra, the cannabinoids — both those produced by our bodies and those found in the plants around us — harmonize with receptors to regulate everything from mood and memory to pain and inflammation.
While much has yet to be uncovered about this system and its myriad effects, the growing interest in cannabinoids presents opportunities for fresh perspectives in medicine, wellness, and beyond. As research continues to unfold, we stand at the precipice of a new era in our comprehension of the delicate balance within our bodies.
the endocannabinoid system invites us to explore the limits of science and nature, reminding us that the quest for knowledge is as dynamic as the systems we endeavor to understand. Here’s to future discoveries that could illuminate even more our shared journey into health and healing.