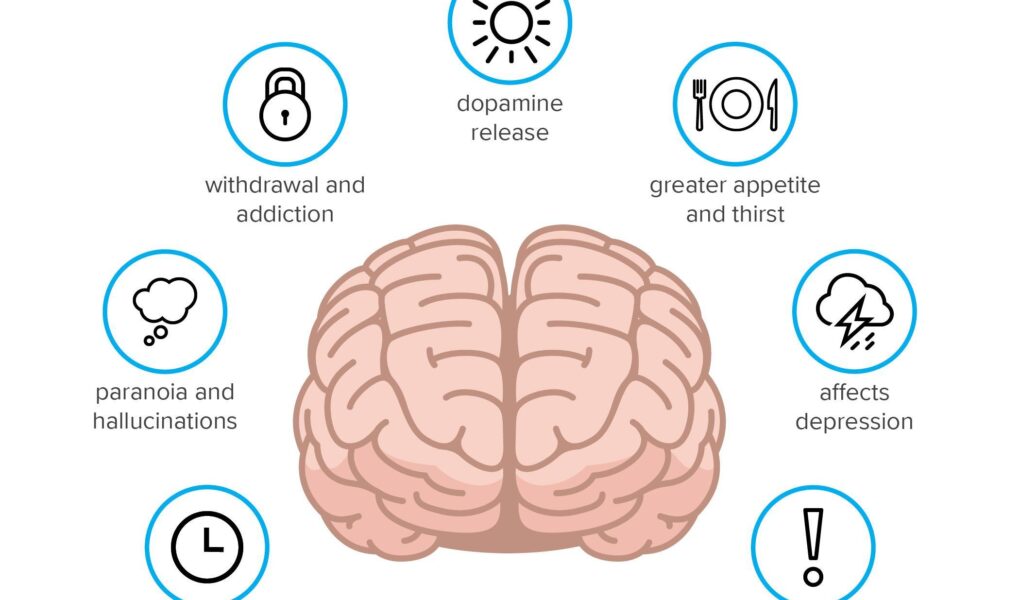
As the clouds of stigma surrounding marijuana continue to dissipate in many parts of the world, a wealth of research emerges, illuminating both its therapeutic benefits and potential drawbacks. While many users tout its positive effects for managing pain, anxiety, and a range of medical conditions, the long-term side effects of marijuana usage invite a more complex conversation. Understanding how this widely consumed substance affects the mind and body over extended periods is crucial for users, policymakers, and health professionals alike. In this article, we delve into the nuanced landscape of long-term marijuana consumption, exploring the various impacts it may have on cognitive function, mental health, and overall well-being. Join us on this journey to unveil the intricacies of a plant that has captivated human curiosity for centuries, as we seek to paint a clearer picture of its enduring effects.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Cognitive Impact of Prolonged Marijuana Use
- Exploring Mental Health Consequences Associated with Long Term Use
- Physical Health Risks: What Chronic Marijuana Consumption May Reveal
- Strategies for Mitigating Long Term Effects of Marijuana on Health
- Q&A
- The Way Forward
Understanding Cognitive Impact of Prolonged Marijuana Use
The prolonged use of marijuana can lead to various cognitive impairments that may affect everyday functioning. Studies have shown that long-term users might experience alterations in their memory and attention span, potentially impacting their academic or professional performance. The brain, particularly during adolescence, is still developing, making it more susceptible to the psychoactive effects of THC, the main active component in marijuana. Some of the cognitive effects observed include:
- Impaired Short-term Memory: Difficulty in recalling recent events or information.
- Decreased Attention: Challenges in maintaining focus on tasks, particularly those requiring sustained mental effort.
- Reduced Decision-making Skills: Impaired judgement and increased risk-taking behaviors.
Furthermore, researchers have pointed to potential alterations in brain structure associated with prolonged marijuana use. These changes can lead to a reduced volume in specific areas, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, which are critical for learning and executive functioning. Below is a simple representation of some of the cognitive changes observed:
| Cognitive Function | Impact of Long-term Use |
|---|---|
| Memory Recall | Impaired short-term and working memory |
| Attention | Diminished capacity to concentrate |
| Learning Ability | Slowed information processing |
| Impulse Control | Increased impulsivity and poor decision-making |
Exploring Mental Health Consequences Associated with Long Term Use
Long-term marijuana use has been linked to various mental health issues that can manifest in different ways. Individuals may experience increased anxiety, which, paradoxically, can lead to a reliance on the substance for relief. Other common mental health consequences include depression and mood instability, which can be exacerbated by the drug’s impact on the brain’s chemistry over time. Studies have suggested that frequent users may find it harder to experience pleasure from everyday activities, leading to a cycle of dependency as they seek out cannabis for temporary reprieve.
Moreover, persistent use can affect cognitive functions, such as memory and attention, making it difficult for individuals to perform well in academic or professional settings. In some cases, there is a risk of psychosis, especially in those with a predisposed vulnerability. This can manifest as a detachment from reality, false beliefs, or hallucinations. A recent study highlights the growing need for awareness regarding these risks:
| Mental Health Issues | Frequency in Long-term Users |
|---|---|
| Anxiety Disorders | 40% |
| Depressive Disorders | 30% |
| Cognitive Impairment | 25% |
| Psychotic Disorders | 15% |
Physical Health Risks: What Chronic Marijuana Consumption May Reveal
Chronic marijuana consumption may lead to a variety of physical health risks that can subtly evolve over time. Users often report respiratory issues similar to those caused by tobacco smoking, owing to the inhalation of smoke that can irritate the lungs. Additionally, long-term usage may disrupt typical cardiovascular functions, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure, elevating the potential for conditions such as arrhythmias. Research suggests that these changes may not just affect adults; adolescents who consume marijuana may experience inconsistent heart development and potential cardiovascular strain.
Beyond respiratory and cardiovascular concerns, the impact of prolonged marijuana use extends to cognitive functions and overall physical health. Studies indicate that heavy users may face challenges such as memory impairment, which can hinder daily activities and learning capabilities. Furthermore, chronic consumption is linked to a decrease in motivation and can have unintended consequences on one’s social interactions and physical fitness levels. Observing long-term users, a few common trends include:
- Increased risk of addiction: Dependence on marijuana can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
- Weight fluctuations: Some users report changes in appetite.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Digestive problems like nausea or stomach pain may arise.
Strategies for Mitigating Long Term Effects of Marijuana on Health
To counteract the potential long-term health effects associated with marijuana use, individuals can adopt several proactive strategies. Limit consumption by establishing clear personal guidelines on usage frequency and quantity can significantly reduce the risk of dependency and associated health issues. Engaging in regular physical activity serves not only to improve overall health but also helps in mitigating some cognitive impacts that prolonged use might entail. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods into one’s diet can support brain and body health, providing essential vitamins and minerals that may be lacking in heavy users. Exploring mindfulness and meditation practices can additionally bolster mental resilience, helping to manage stress and anxiety without reliance on substances.
For those looking to transition away from regular use, consider participating in support groups or therapy tailored for substance use, which can provide community and accountability. It may also be beneficial to utilize alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or yoga, to reduce symptoms of withdrawal and to enhance mental clarity. Developing a strong social support network can play a crucial role in maintaining motivation and resilience throughout this process. Below is a table summarizing these strategies and their potential benefits:
| Strategy | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Limit consumption | Reduced dependency risk |
| Regular physical activity | Improved cognitive function |
| Mindfulness and meditation | Enhanced stress management |
| Support groups | Community and accountability |
Q&A
Q&A: The Long-Term Side Effects of Marijuana
Q1: What are the long-term effects of marijuana use?
A1: Long-term marijuana use can lead to a range of effects, both physical and psychological. Users may experience respiratory issues due to habitual smoking, heightened anxiety or paranoia, cognitive impairments such as memory problems, and potential addiction. Additionally, prolonged use can impact motivation and decision-making skills, often referred to as ”amotivational syndrome.”
Q2: Can marijuana affect mental health over time?
A2: Yes, research suggests that long-term marijuana use can exacerbate mental health issues. Individuals predisposed to conditions like depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia may find their symptoms intensified. It is important to note that the relationship between marijuana and mental health is complex and varies from person to person.
Q3: How does long-term marijuana use impact cognitive function?
A3: Studies indicate that long-term marijuana use may affect cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and learning. Chronic users may have difficulty with tasks that require concentration and multitasking. Some of these effects may diminish after cessation, but others may persist, especially with early or heavy usage.
Q4: Are there any potential benefits associated with long-term marijuana use?
A4: While focusing on the side effects is essential, it’s also worth noting that some individuals report long-term benefits from marijuana, such as improved management of chronic pain, reduced inflammation, and enhanced quality of life in certain medical conditions. It’s crucial to balance these potential benefits with an awareness of the possible risk factors involved.
Q5: How does frequency of use affect the likelihood of experiencing long-term side effects?
A5: Frequency and amount of use play significant roles in determining the likelihood and severity of long-term side effects. Regular, heavy use, especially when started at a young age, typically correlates with a higher risk of adverse effects. Conversely, occasional use may result in fewer or less severe side effects, though individual responses can vary widely.
Q6: Is it possible to reverse the long-term effects of marijuana use?
A6: Many of the negative long-term effects can improve with cessation of use, although this can depend on the duration and intensity of usage. Cognitive and psychological issues may take time to improve, and some effects, particularly those related to long-standing mental health conditions, might require professional treatment to address.
Q7: What should individuals consider before using marijuana long-term?
A7: It’s essential for individuals to weigh the benefits and risks unique to their circumstances. Consulting healthcare professionals for tailored advice is advisable, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or concerns. Moreover, being informed about local laws, potential addiction, and personal health history can guide better decision-making.
Q8: Are there differences in effects between smoking marijuana and using other forms, like edibles or oils?
A8: Yes, the method of consumption can influence the effects experienced. Smoking marijuana typically leads to a quicker onset of effects, which may alter dosage control and increase dependence. Edibles and oils, on the other hand, produce prolonged effects but can lead to inadvertent overconsumption. Each method has its own profile of potential long-term effects and health implications.
By addressing these questions, we hope to provide a nuanced understanding of the long-term side effects of marijuana, allowing individuals to make more informed choices about their use.
The Way Forward
As we draw the curtains on our exploration of the long-term side effects of marijuana, it’s essential to recognize the complexity of this subject. Like many elements of our lives, the impact of cannabis can vary significantly from person to person, influenced by factors such as genetics, frequency of use, and individual health profiles. While some may celebrate the therapeutic and recreational aspects of marijuana, it is crucial to remain informed about the potential risks that accompany its consumption.
As society continues to navigate the evolving landscape of cannabis legalization and acceptance, understanding these long-term effects empowers individuals to make choices that are right for them. Ultimately, the dialogue surrounding marijuana should remain open and nuanced, encouraging personal responsibility and informed decision-making. knowledge is the most potent tool in ensuring that our experiences with cannabis are safe, responsible, and enriching.