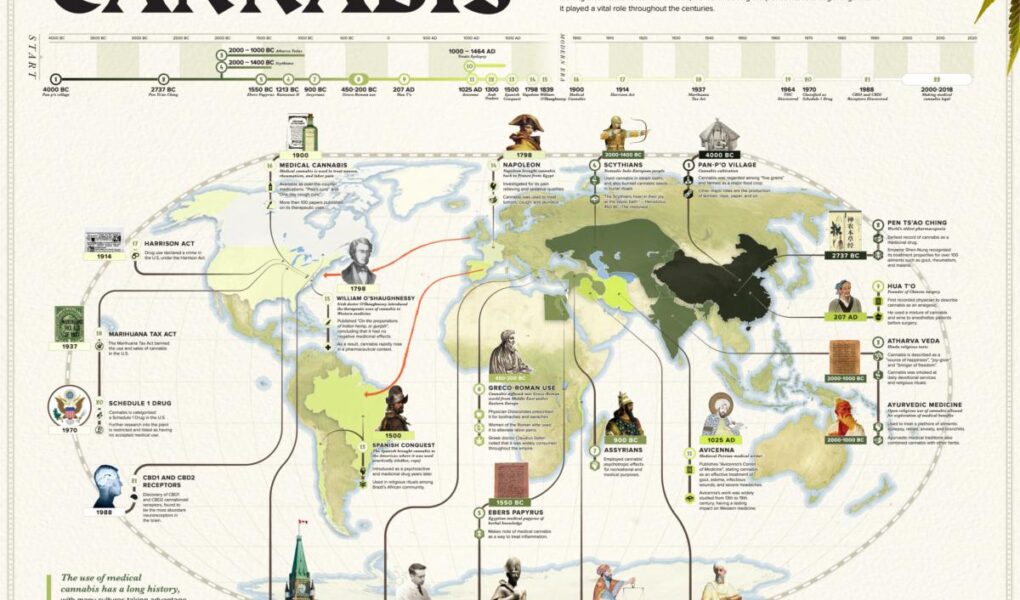
The Journey of Cannabis: A Verdant Tale Through Time
From the ancient fields of China to modern-day dispensaries, the cannabis plant has a rich and multifaceted history that reflects the evolving relationship between humanity and nature. Once revered as a sacred herb by ancient civilizations, cannabis has journeyed through eras of cultivation, prohibition, and resurgence, leaving an indelible mark on culture, medicine, and legislation across the globe. As we unravel the story of this versatile plant, we encounter a narrative woven with threads of tradition and innovation, conflict and reconciliation. Join us as we explore the historical milestones that have shaped cannabis, illuminating its roles as both a source of healing and an emblem of social change throughout the ages.
Table of Contents
- Origins and Evolution of the Cannabis Plant
- Cultural Significance Throughout the Ages
- Medicinal Uses and Research Developments
- Contemporary Legal Landscape and Future Directions
- Q&A
- The Conclusion
Origins and Evolution of the Cannabis Plant
The cannabis plant, scientifically known as Cannabis sativa, has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Originating in Central Asia, it has evolved alongside humanity, adapting to various climates and cultivation techniques. Early records indicate that ancient cultures utilized cannabis for various purposes, including:
- Textiles: The fibers of the cannabis plant were used to make clothes, ropes, and paper.
- Medicinal Uses: Ancient texts from China and India document the therapeutic applications of cannabis for treating a range of ailments.
- Religious Significance: In several cultures, cannabis was employed in spiritual rituals, symbolizing a connection between the earthly and the divine.
As civilizations expanded and trade routes intersected, cannabis spread globally, leading to its cultivation in various regions. Over the centuries, distinct varieties emerged, each with unique adaptations and properties. Today, cannabis is classified primarily into three subspecies:
| Subspecies | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Cannabis sativa | Known for its tall structure and uplifting effects; commonly used for recreational and industrial purposes. |
| Cannabis indica | Shorter and bushier, this subspecies is recognized for its relaxing effects, often utilized in therapeutic contexts. |
| Cannabis ruderalis | A lesser-known variety, primarily found in Eastern Europe and Russia; typically lower in THC and often used in hybrid strains. |
Cultural Significance Throughout the Ages
The cannabis plant has woven itself into the fabric of human culture for thousands of years, serving various roles across civilizations. In ancient China, it was revered not just for its psychoactive properties but also for its medicinal uses. The traditional Chinese medicine system incorporated cannabis seeds and leaves as remedies for ailments ranging from pain relief to digestive issues. Meanwhile, in ancient India, cannabis became central to spiritual rituals, with its use in Bhang, a traditional drink made from ground cannabis leaves, adding layers to religious celebrations. This multi-faceted plant has also been a part of artistic and literary expressions, where it was celebrated for its capacity to enhance creativity and perception.
As cannabis cultures evolved, it transcended borders and was integrated into various social frameworks. In the Turkish empire, hashish became synonymous with poetic gatherings, while in the Middle East, it found a place within Sufi traditions, serving as a tool for reaching transcendental states of awareness. Across African tribes, hemp fibers were utilized for crafting textiles and cordage, showcasing the plant’s versatility beyond its psychoactive properties. The influence of cannabis can even be tracked through historical trade routes, where it was exchanged among merchants and travelers, fostering interconnectedness through shared cultural practices. Today, the revival of interest in cannabis can be seen as a reconnection with ancient knowledge, blending history with modern understanding in a global dialogue.
Medicinal Uses and Research Developments
The therapeutic potential of the cannabis plant has gained significant attention in recent years, leading to groundbreaking research and a reevaluation of its role in medicine. Traditionally used for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, cannabis has been at the forefront of treating various ailments. Key medicinal applications now include:
- Pain Management: Effective in alleviating chronic pain conditions.
- Anti-nausea: Particularly beneficial for chemotherapy patients to combat nausea and vomiting.
- Appetite Stimulation: Helps increase appetite in patients with conditions like HIV/AIDS.
- Seizure Reduction: Cannabidiol (CBD) has shown promise in reducing seizures in epilepsy patients.
Recent research developments have further illuminated the complex relationship between cannabinoids and the human endocannabinoid system, paving the way for new therapeutic formulations. Innovative studies are exploring the entourage effect, where different cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically to enhance medicinal benefits. Some ongoing research efforts focus on:
- CBD for Anxiety Disorders: Trials investigating the anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol.
- THC for Glaucoma: Exploring tetrahydrocannabinol’s potential to lower intraocular pressure.
- Phytocannabinoid Pharmaceutics: Developing concentrated extracts for targeted therapies.
| Condition | Cannabinoid | Research Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic Pain | THC | Reduces pain sensation in clinical trials. |
| PTSD | CBD | Helps mitigate anxiety and trauma-related symptoms. |
| Multiple Sclerosis | THC/CBD | Improves spasticity and mobility issues. |
Contemporary Legal Landscape and Future Directions
The evolution of cannabis legality has been a journey marked by shifting perceptions and regulatory challenges. Various jurisdictions have embraced legislation that reflects a growing acceptance of both therapeutic and recreational use. In recent years, several key trends have emerged, shaping the present landscape and hinting at future directions:
- Decriminalization and Legalization: More regions are moving towards full legalization, recognizing the economic potential and public health benefits of regulated cannabis markets.
- Medical Use Expansion: Many states and countries are now acknowledging the therapeutic benefits of cannabis, leading to an increase in patient access and research opportunities.
- Regulatory Framework Improvements: With legalization has come the need for robust frameworks governing everything from cultivation to distribution, ensuring safety and compliance.
As society continues to reassess its stance on cannabis, the focus on sustainability and innovation within the industry is becoming paramount. Stakeholders are beginning to explore how to cultivate cannabis in an environmentally responsible manner, paving the way for practices that not only comply with regulations but also promote ecological health. The future may very well see:
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in technology could streamline production and enhance product quality, making cannabis more accessible.
- Cross-Border Trade: As more regions adopt favorable regulations, the potential for international trade in cannabis products expands.
- Increased Public Education: Ongoing public discourse and education efforts will be essential to mitigate misconceptions and promote responsible use.
Q&A
Q&A: The History of the Cannabis Plant
Q1: What is the earliest known use of cannabis by humans?
A1: The earliest documented use of cannabis dates back to around 5000 BCE in Central Asia, where it was cultivated for its fibers. Archaeological evidence points to its application in textiles and rope-making, showcasing early human ingenuity in utilizing the plant’s versatile properties.
Q2: How did cannabis’ role evolve in ancient cultures?
A2: In ancient cultures, cannabis transitioned from a utilitarian plant to one imbued with spiritual significance. The Ancient Chinese recognized its medicinal qualities, while the Scythians, around the 5th century BCE, inhaled the smoke of burning cannabis seeds and flowers during rituals. This duality of use—practical and mystical—was common across various civilizations.
Q3: When did cannabis start being used for medicinal purposes?
A3: The medicinal use of cannabis can be traced back to Ancient China. The renowned physician Shen Nong mentioned cannabis in his herbal texts around 2737 BCE, referring to its use for treating ailments such as pain and digestive disorders. Its therapeutic potential was acknowledged in other cultures, including the Egyptians and Greeks, who valued it for its various health benefits.
Q4: How did the perception of cannabis change through the ages?
A4: Throughout history, cannabis has experienced fluctuating perceptions. In the 19th century, it enjoyed a renaissance as a medicinal resource in Western medicine, appearing in tinctures and pharmaceuticals. However, by the early 20th century, global sentiment shifted, fueled by moral panic and misinformation, leading to its criminalization and stigmatization in many parts of the world.
Q5: What role did cannabis play in the social and political landscape of the 20th century?
A5: Cannabis became a focal point in the social and political upheaval of the 20th century, particularly during the 1960s cultural revolution. It was intertwined with movements advocating for civil rights and anti-establishment sentiments. This association, combined with legislative restrictions, contributed to the complex tapestry of cannabis’ perception as both a symbol of rebellion and a target of law enforcement.
Q6: How has the recent legalization movement influenced the understanding of cannabis?
A6: The recent wave of legalization—beginning in the late 20th century and accelerating in the 21st—has sparked renewed interest in the cannabis plant. This movement emphasizes research into its medicinal potential and challenges the stigmas that have surrounded it. As more states and countries embrace legalization, cannabis is gradually being reclassified from a dangerous substance to a legitimate agricultural product with various uses, from medical applications to industrial hemp.
Q7: What does the future hold for cannabis as a plant and a cultural symbol?
A7: The future of cannabis seems poised at a crossroads where science and tradition converge. As research expands our understanding of the plant’s properties and benefits, we can anticipate an increasingly prominent role in both medicine and consumer markets. Moreover, as societal perceptions continue to evolve, cannabis may cement its place not just as a controversial topic but as a multifaceted cultural symbol of healing, sustainability, and even economic opportunity.
Q8: How can individuals engage with the history of cannabis today?
A8: Individuals can explore the history of cannabis through various channels such as literature, documentaries, and museums dedicated to its cultural impact. Participating in informed discussions, advocating for responsible legislation, and supporting efforts to destigmatize the plant are also powerful ways to connect with cannabis’ rich history while fostering a future characterized by understanding and respect.
The Conclusion
As we close the pages of this exploration into the history of the cannabis plant, we find ourselves at a fascinating crossroads of tradition and modernity. From its ancient roots as a multifaceted resource in various cultures to its contemporary role in the fields of medicine, industry, and social reform, cannabis has continually evolved, reflecting humanity’s shifting perceptions and needs.
The journey of this remarkable plant is not merely a chronicle of its uses but a mirror to our societies—shedding light on issues of legality, ethics, and consciousness. As we move forward, it is essential to consider not only its rich past but also the possibilities that lie ahead. The debate surrounding cannabis remains vibrant and complex, intertwined with questions of health, justice, and sustainability.
In understanding the history of cannabis, we gain insight not just into the plant itself, but into the broader narrative of human civilization—our relationship with nature, our evolving values, and our ongoing quest for knowledge. As we look towards the future, let us engage in thoughtful dialogue and informed decision-making, honoring both the legacy of the cannabis plant and the diverse perspectives that shape its place in our world.